Have you just finished building your first website? Want to give it the best start possible? Want to know what the pros do to ensure their WordPress website is ready to take on the world?
Installing WordPress is the first step toward building a great website. Your work isn’t over yet though. We recommend taking a few more simple steps to make it perfect for your audience.
What if we provide a complete checklist that you can download and print, a checklist you can refer to every time you create a new website from scratch?
It’s a great idea to begin your journey with confidence that will undoubtedly increase your chances of success.
So, how can you tweak, and what are the steps involved to optimize your site?
By implementing this list, you will have a website ready for a successful journey.
First, let us familiarize you with the backend where all the action happens, and then jump to our list of the most important things you need to do after installing WordPress.
They can all contribute to making your site awesome!
We have also described most of these steps in a video to help you visually learn how to perform these essential things after installing WordPress.
- 1. WordPress dashboard tour
- 2. Site identity
- 3. General settings (email address, site language, time zone)
- 4. Permalinks
- 5. Discussion (essential settings to optimize commenting)
- 6. Clean WordPress and delete default entries
- 7. Gravatar (change your display image)
- 8. Complete your user profile
- 9. Install a WordPress theme (Astra)
- 10. Customize your website design
- 11. Create or edit categories
- 12. Create menus
- 13. SEO optimization
- 14. Set up Google console
- 15. Submit a sitemap
- 16. Robots.txt file
- 17. Google Analytics
- 18. Website security
- 19. W3 Total Cache for website performance
- 20. Optimize for conversion
- 21. Privacy policy
- 22. Create users
- 23. Publish a post
- 24. Limit post revisions
- 25. Set up ping services
- 26. Brand your login page
- Final Thoughts
1. WordPress dashboard tour
Whatever you see on your screen on a WordPress website is managed from the dashboard. We also call it the WP admin panel, WP admin or admin area.
It’s up to you which term you use the most, but it is helpful to learn what it’s all about.
Being a WordPress user, you will spend considerable time inside the dashboard for:
- Creating and managing content
- Connecting with fans, readers and customers
- Adding new features through plugins
- Customizing the design through themes
- Hardening security and optimizing site performance through different options and plugins
As you’re new to WordPress, we think you should know about different segments of the dashboard.
We suggest not skipping this part unless you already know the whole dashboard, as this will go a long way to helping you become a more proficient user.
You can access WP admin by adding /wp-admin to your website URL.
For example, www.yoursitename.com/wp-admin or, more precisely, www.yoursitename.com/wp-login.php.
Both ways take you to your site’s login screen.
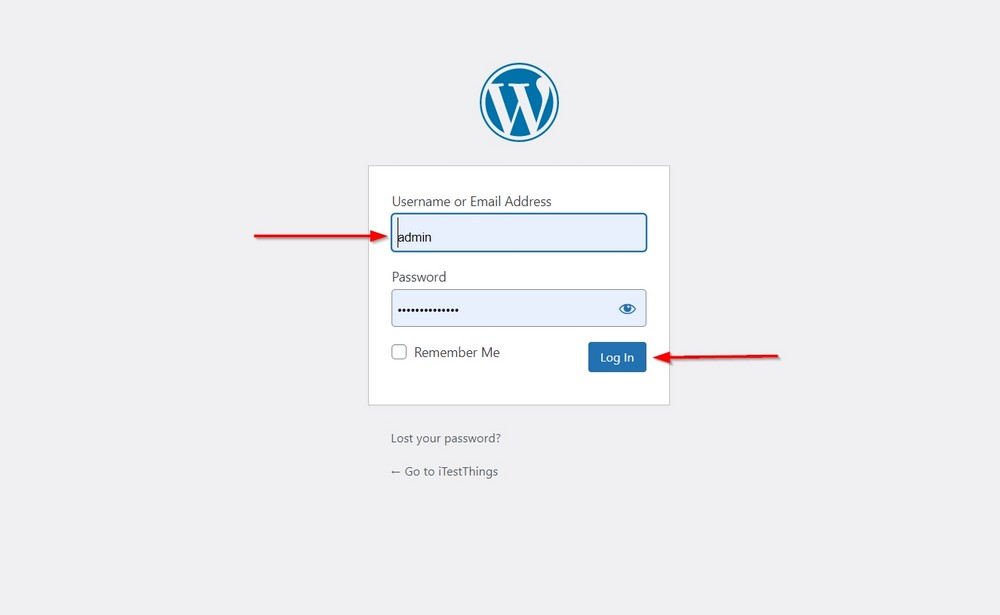
Enter the username and password you created when installing WordPress and press the Log In button.
We suggest changing the user name from admin to something challenging for security reasons. It’s too common and easy to guess by hackers.
You can do it at the time of WordPress installation or by adding another user. We will discuss this part later in the article.
Once logged in, you should see the WordPress dashboard.
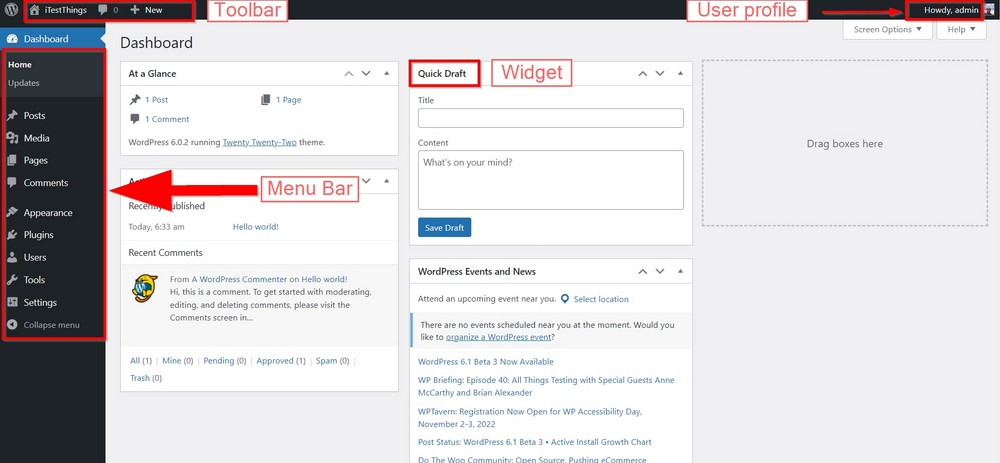
The larger pane on the right shows different widgets, including Quick Draft, Site Health, WordPress events and news, At a glance and Activity.
They are all informative widgets and shortcuts to specific functions. You can add widgets by selecting one and dragging it into the center pane.
You can also hide them all from the Screen Options visible at the top right corner.
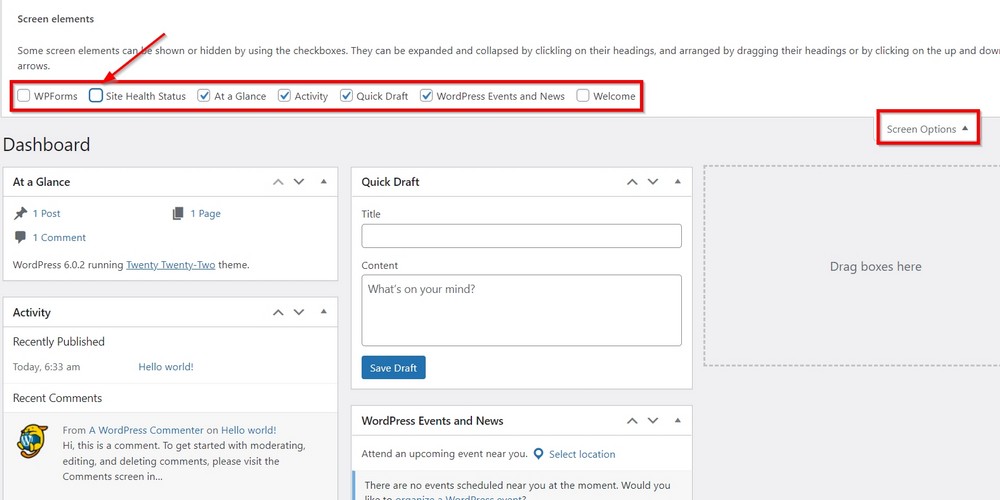
Roll down the menu by clicking a small arrow beside Screen Options and check/uncheck the widget you want on your screen.
The left sidebar has all the menu items you will regularly use for performing different functions on your website.
A toolbar at the top of the page offers several shortcuts to the left sidebar menu items. These menus will expand as you add more plugins to your site.
2. Site identity
Site identity is essential for every website.
The site title and tagline explain what the site is about. Plus, it is valuable for Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
To set them, go to Appearance > Customize > Site Identity and add the desired information.
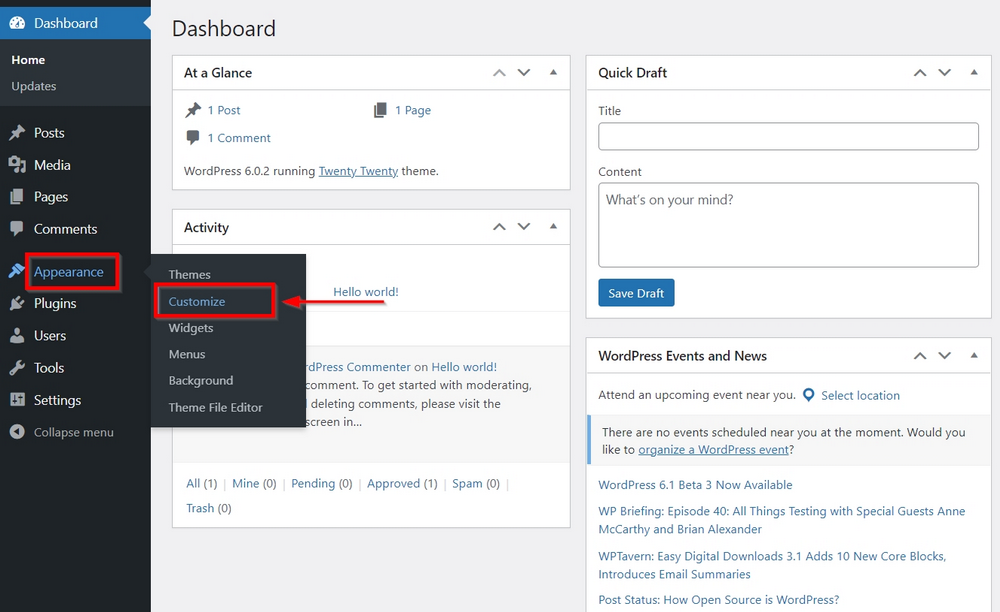
We are building an example website that sells bicycles so we will add the following title and tagline. You can change what suits your needs.
Title: JD Cycles
Tagline: The Best Sports Cycles
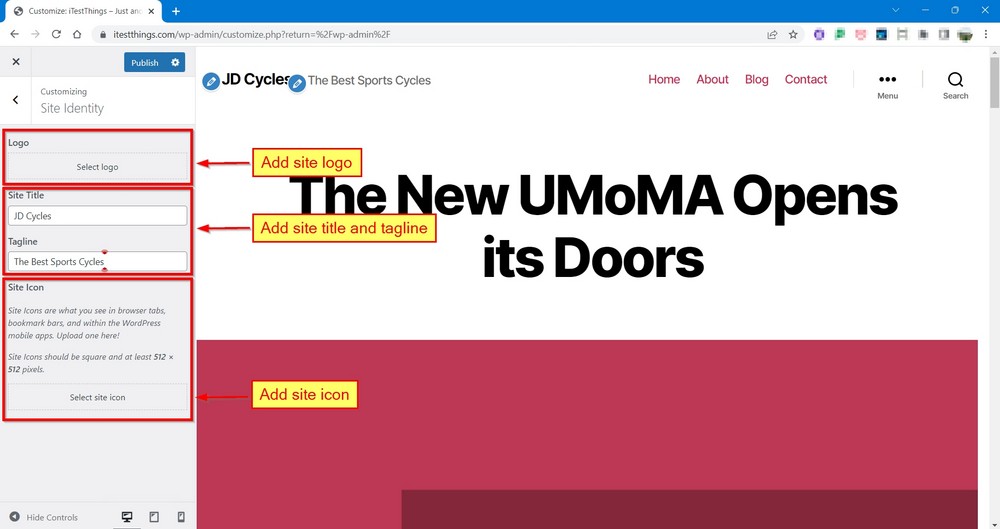
Alternatively, you can set the title and tagline from Settings > General.
We chose the first option because we can add a logo and site icon from the same screen.
So to add a logo and icon, press the buttons and upload images.
Once you are done with the title, tagline, logo, and icon, press the Publish button on top to save changes.
Pro Tip:
You’ll need to save any changes for every page or tab you use in WordPress. Get used to it quickly to save having to go back and repeat your work!
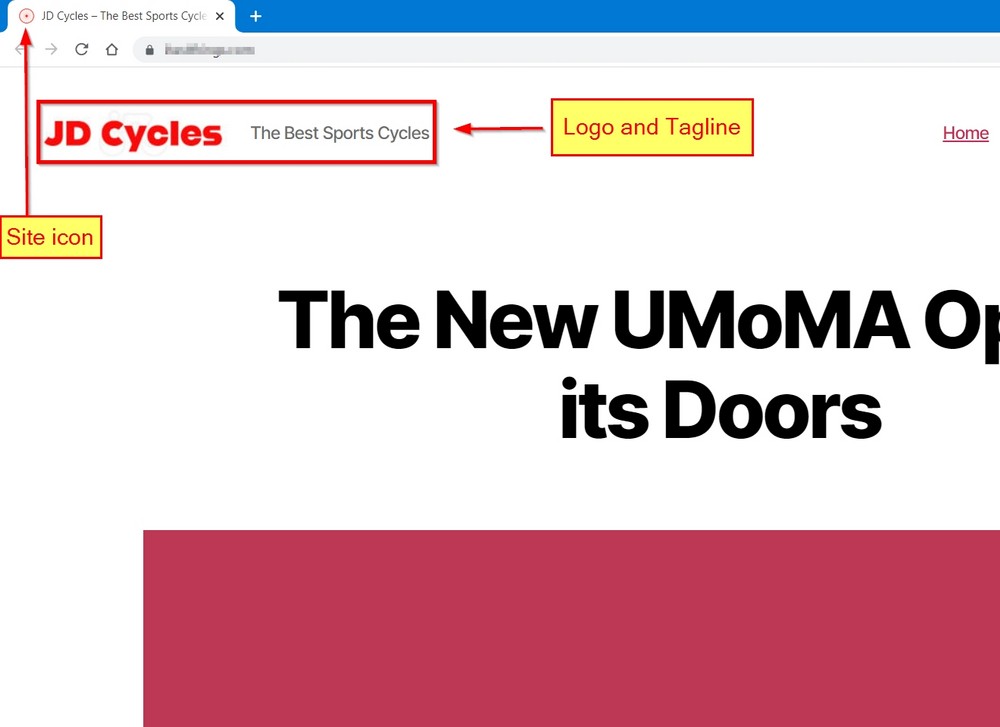
You will notice that after uploading the logo, it will replace the site’s title, which is normal.
3. General settings (email address, site language, time zone)
Next, go to Settings > General to change a few things. These settings are essential for your site’s general functionality.
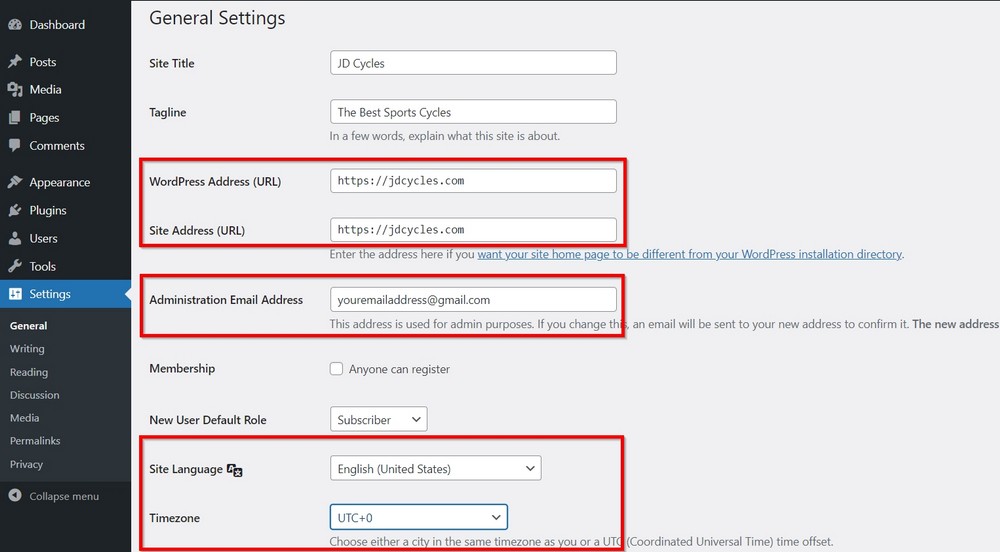
WordPress Address URL and Site Address URL fields are filled by default when you install WordPress. Make sure the URLs are correct and similar in both fields.
You’ll want to make this identical to the URL you bought when setting up your website.
You can change the Administration Email Address on this page which was added during installation. It’s the primary email address WordPress will use to send alerts.
For example, when a user leaves a comment, WordPress will send a notice to this address.
It also becomes the default email address for the first user. If you need to replace it with another email address, you can.
You can also change your site’s language by choosing one from the Site Language field related to your site.
And similarly, select a Timezone that is according to where your business address is located.
Save any changes you made.
4. Permalinks
Go to Settings > Permalinks to find out different preset URL structures WordPress offers. Permalinks control the URL structure of your website.
It is something you need to fix before telling Google and other search engines to index your site.
In our list of things to do after installing WordPress, we suggest you choose the permalink as early as possible.
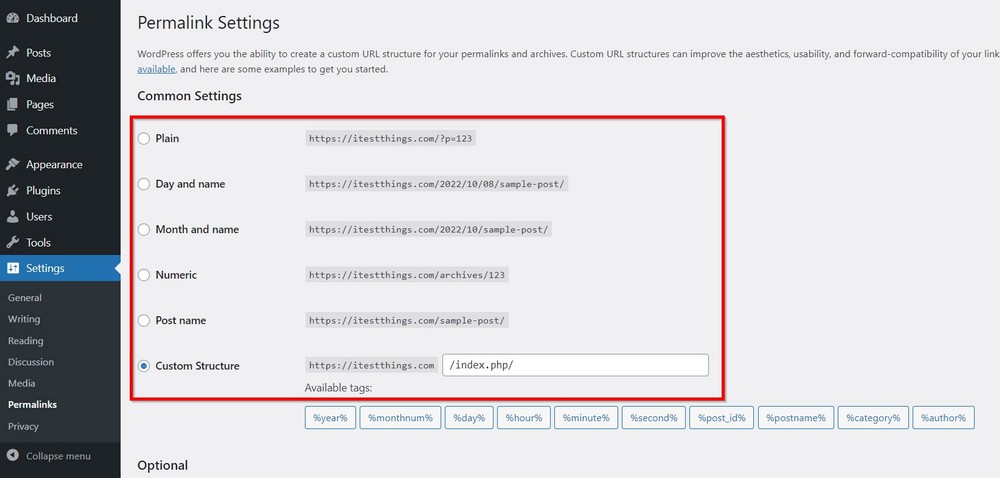
Choose the one that you think is suitable for your website.
You can use the Custom Structure and Available tags underneath to design a custom structure according to your needs.
Pro Tip:
We suggest going with Post name. It keeps the URL short, and it is most effective for SEO.
Save any changes you made.
5. Discussion (essential settings to optimize commenting)
The Discussion page is where you can allow or disallow comments on your website.
If engaging with users through comments is a part of your business plan, you can optimize it from here.
Go to Settings > Discussion to open the page. You will notice lots of options and checkboxes under different segments.
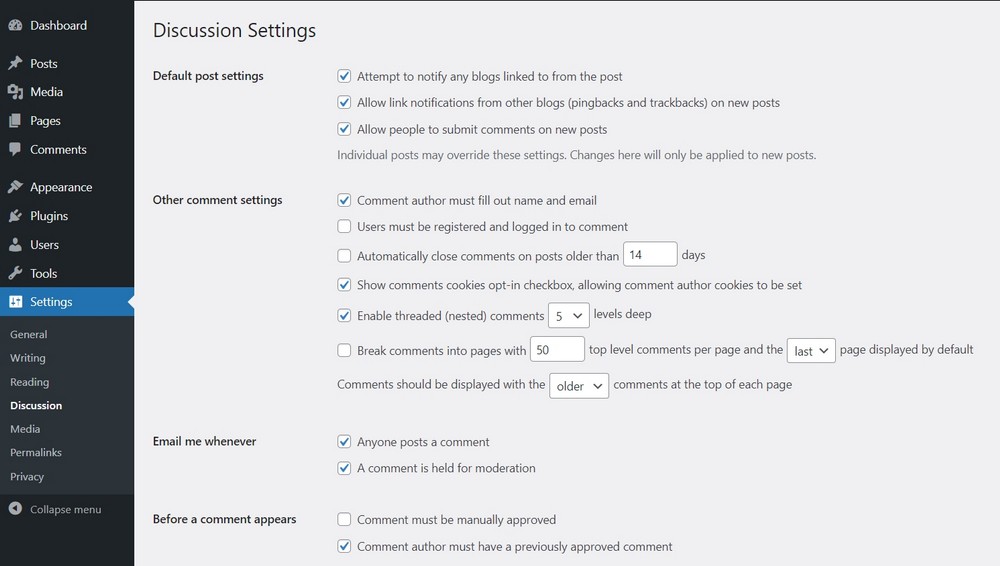
By default, WordPress publishes every comment that comes in.
You can change any of the following settings depending on your needs:
- To disable comments on your website, uncheck the option Allow people to submit comments on new posts.
- If you want to allow registered users to comment, check the option Users must be registered and logged in to comment.
- To stop spam comments from being published automatically, check the option Comment must be manually approved.
- If you want to moderate a comment with at least one hyperlink, change the value from 2 to 1 in the Moderation Section section.
- If you know comments with specific words will always be spam, make a list of those words and put it inside the Disallowed Comment Keys field.
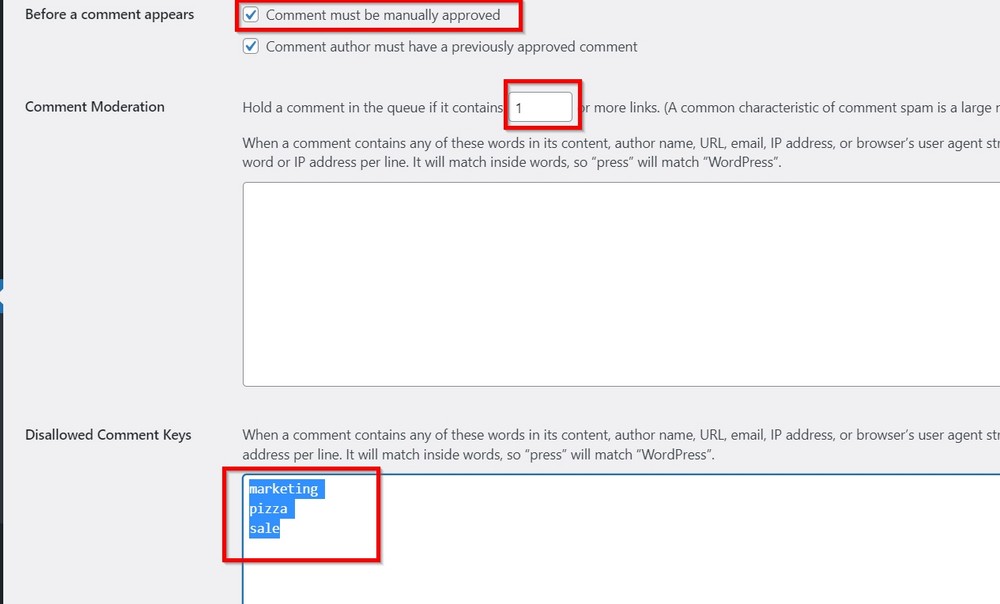
Press the Save Changes button at the bottom of the page once you’re finished.
6. Clean WordPress and delete default entries
Next, let’s do a little housekeeping. It isn’t essential but it’s definitely useful.
A: Delete posts
After installing WordPress, you will notice it comes with some sample content, including a post, a sample comment, a few pages, and plugins.
You can clean this up by accessing each section and removing the content you don’t need.
Select Posts > All Posts.
You should see a default post with the title Hello World!
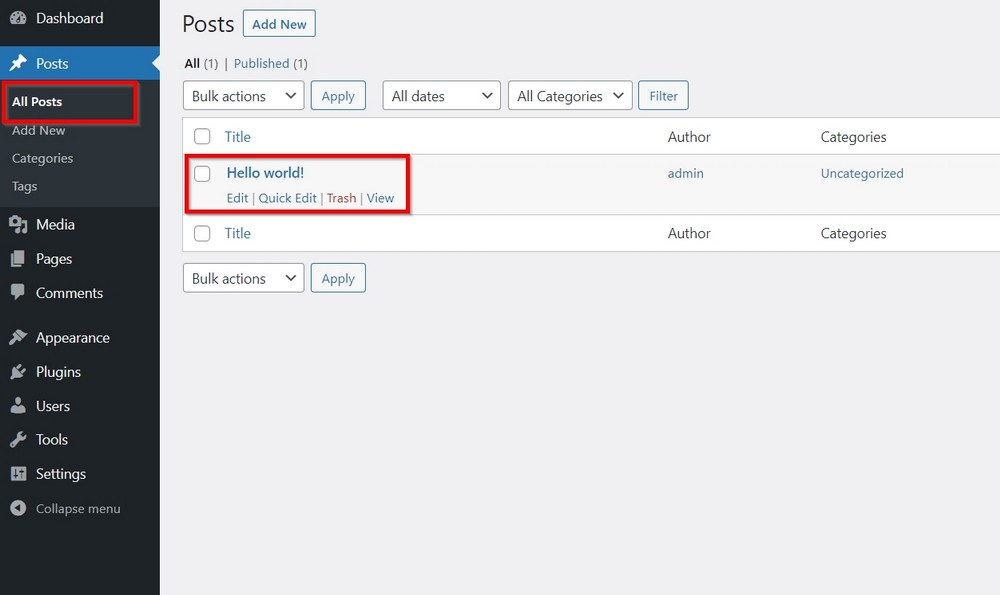
It is an introductory post for every WordPress user to explain how a published post will look. It adds no real value to your website.
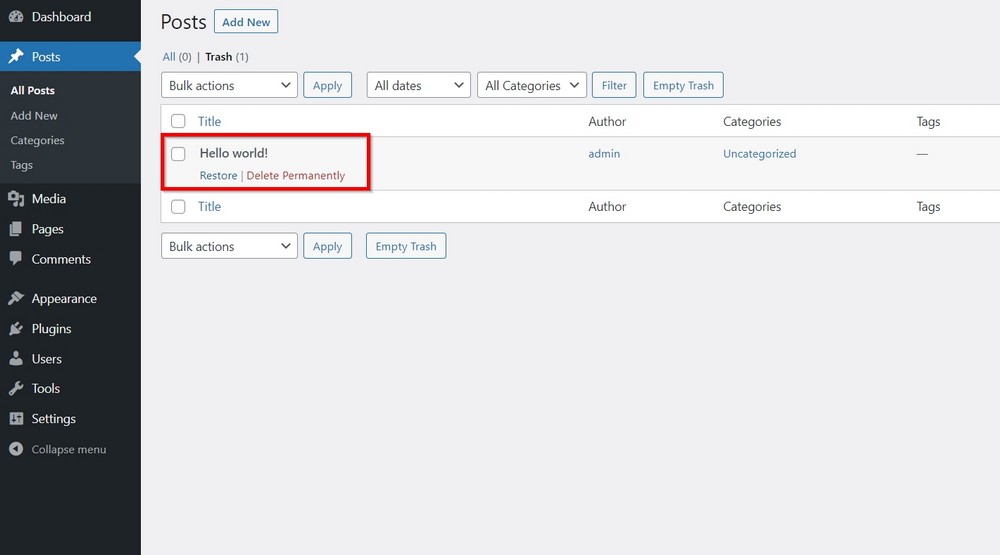
Hover your mouse over the title to bring out a small menu bar underneath. You will see Edit, Quick Edit, Trash, and View options.
You can click on View to see the post’s content and Trash to delete it.
Pro Tip:
If you accidentally delete a post and decide to bring it back later, you can go to the Trash page, hover your mouse over the title and click on Restore.
You can also press Delete Permanently to remove it forever.
B: Delete pages
You can repeat the same process for pages and remove any you don’t need.
Go to All Pages from the sidebar menu to find the default pages WordPress created during installation.
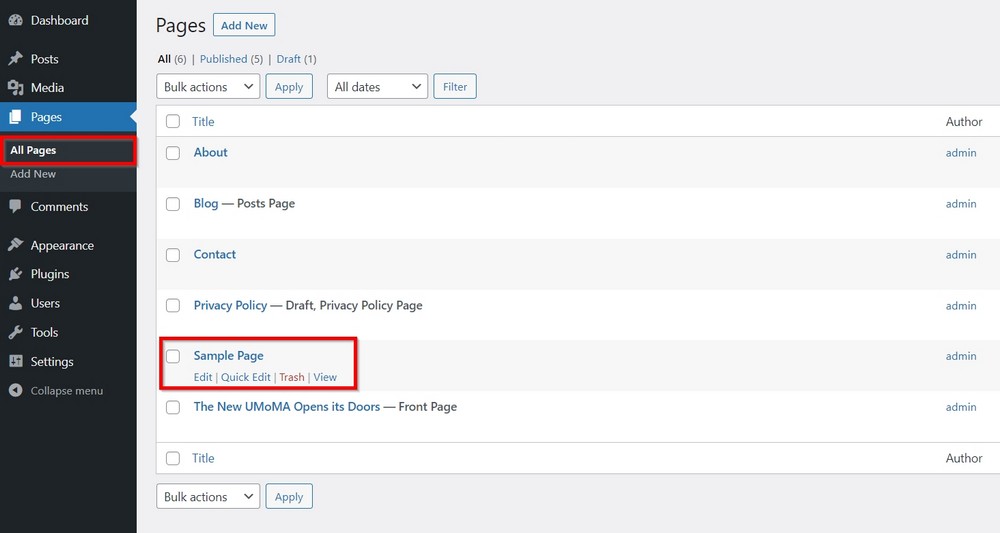
You can delete any or all pages as you need. Though the About, Contact, and Home pages are crucial for your website, you can delete them for now.
We will show you how to create them with a bit of style in a little while.
For deleting all pages at once, click on the checkbox you can find on top beside Title.
This will check all the visible pages, move to the Bulk actions dropdown field on top or bottom.
Then select Move to Trash. This will delete all pages for you.
C: Deactivate plugins you don’t need
Web hosts sometimes install plugins on your website when installing WordPress. These are just the recommendations and sometimes promotions you can consider for your future needs.
You can remove them and install better alternatives from the WordPress plugin repository.
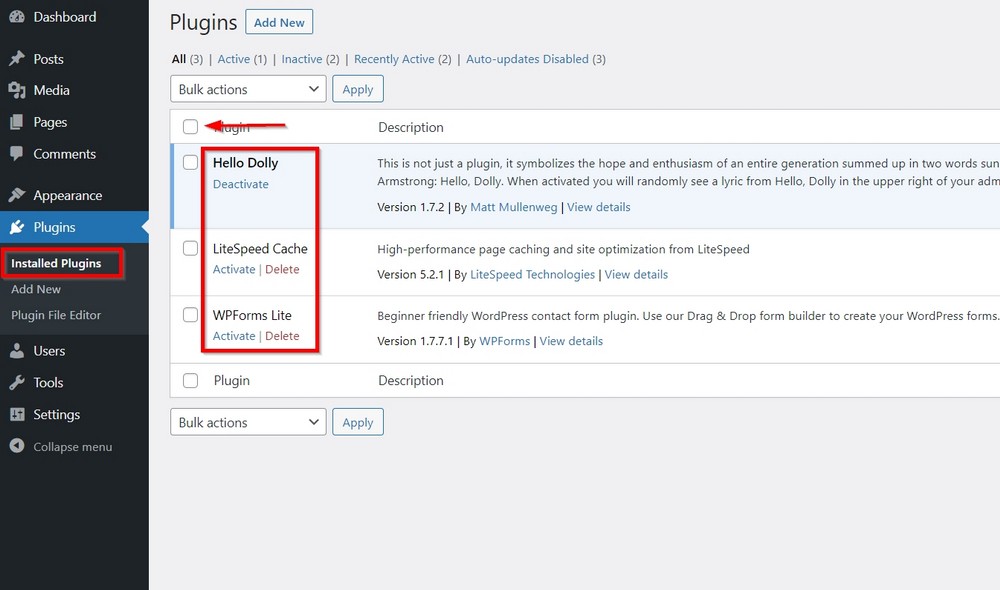
Go to Plugins > Installed Plugins and select all.
Select Delete from the bulk actions dropdown field, and press the Apply button. That’s it.
You can deactivate or delete an individual plugin too if you prefer.
7. Gravatar (change your display image)
Gravatar is the profile picture visible on your site as an author of the post and comment. It is also visible in the top right corner when you are logged in as a WordPress user.
Gravatars can be useful when you have a community but are linked to slowing down websites. It’s up to you whether you use them or not.
If you do want to use Gravatar, you can choose anything, your image, company logo, or a visual icon you will prefer for your identity.
To upload an image, sign up at www.gravatar.com and add your desired picture. You should use the email that you used for WordPress.
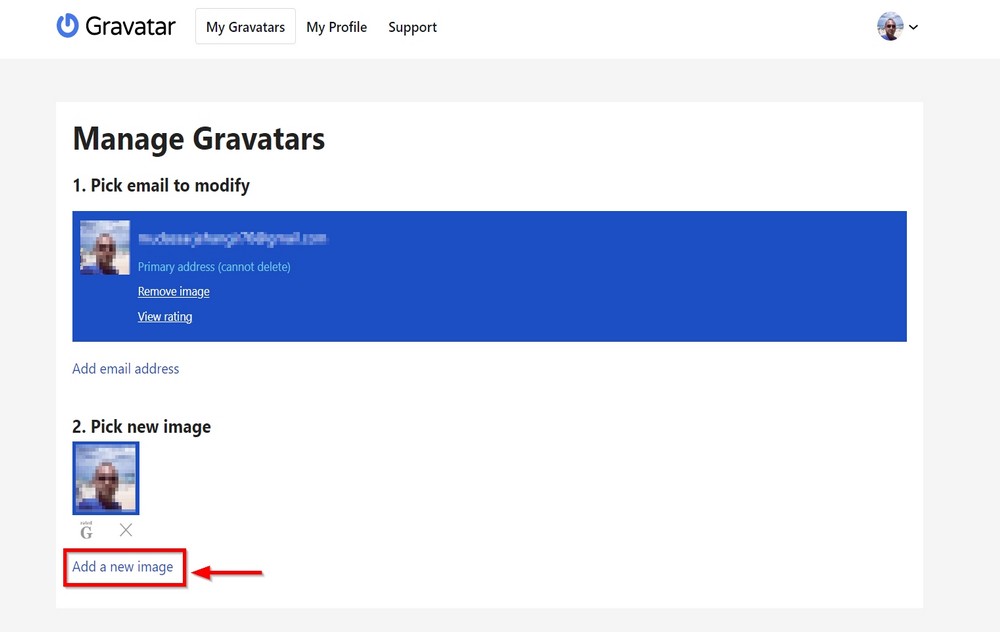
Click on Add a new image and upload an image from your computer. That’s it.
It may take a few minutes before it starts to show in your WP admin.
If you don’t want to use Gravatar select Settings > Discussions and uncheck the box next to Avatar Display.
8. Complete your user profile
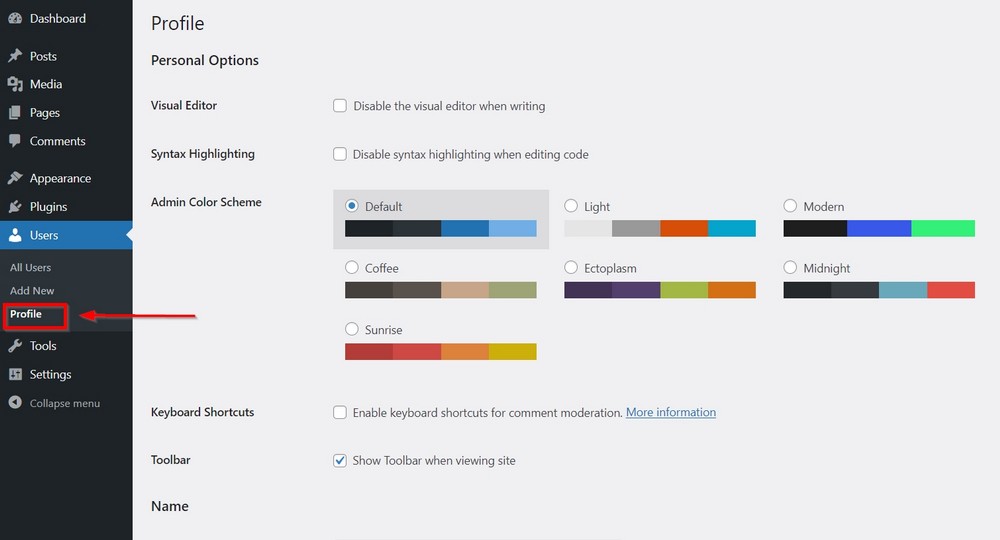
To update your user profile, go to Users > Profile.
It’s a long page that allows you to set a number of things that are useful for your identity on your site.
They include:
- Your name
- Nickname
- Display name
- Biographical info
- Resetting password
- Admin color scheme
The default settings will typically work perfectly well, but you are free to change anything you like.
Just remember to save if you do make changes.
9. Install a WordPress theme (Astra)
A WordPress theme controls how your website looks and feels to the audience. There are thousands of WordPress themes available. Some will be free while others need to be paid for.
We typically prefer websites that are stunning and loaded with features. Performance is something we often ignore while looking for a captivating theme.
We shouldn’t!
We believe all three elements – beauty, features, and performance – go hand in hand.
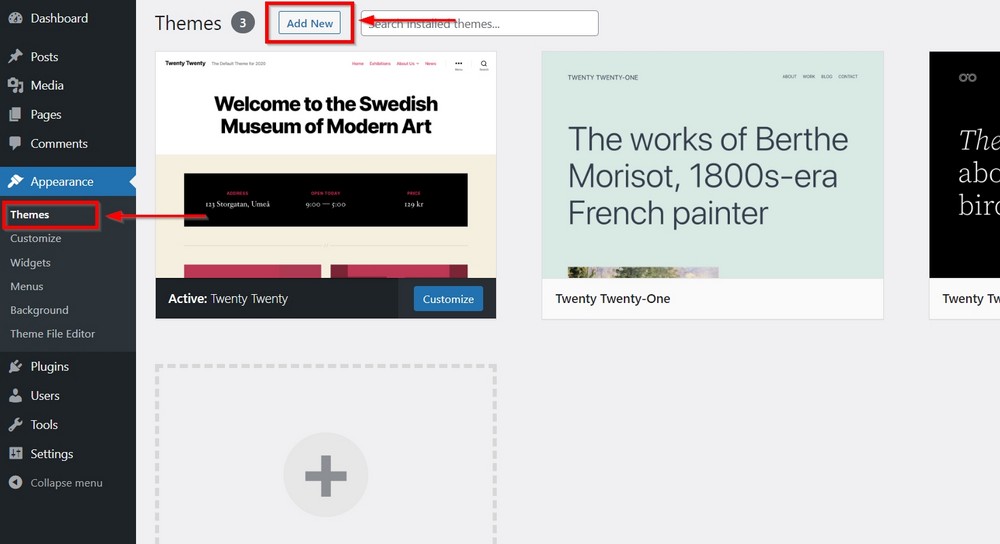
Let’s find and install a theme that checks all three boxes.
Go to Appearance > Themes and search for Astra.
Press the blue Install button and press Activate when the option appears.
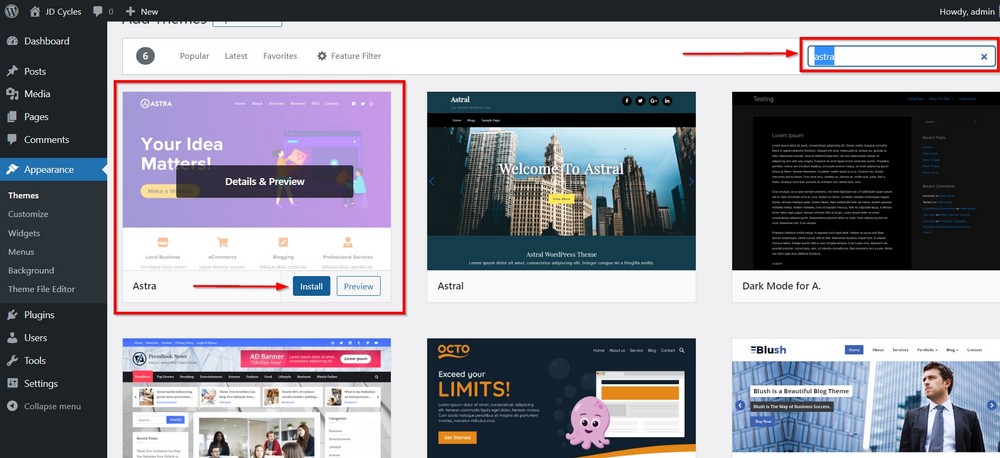
Astra is developed by us and is one of the most popular WordPress themes, with over 1.7 million active installations and over 5,000 five-star ratings.
It’s also free and great for beginners.
Once Astra has been installed and activated, you can delete any themes you don’t plan to use.
Click on a theme you want to remove from your site.
Press the red Delete link at the bottom right corner of the theme window.
Repeat this for every theme you wish to delete.
10. Customize your website design
Redesigning your website is easy with Astra as it offers a massive template library.
A: Install the Starter Templates plugin
Astra offers hundreds of predesigned templates for multiple niches.
To access the Astra template library, you’ll need to install Astra’s Starter Templates plugin.
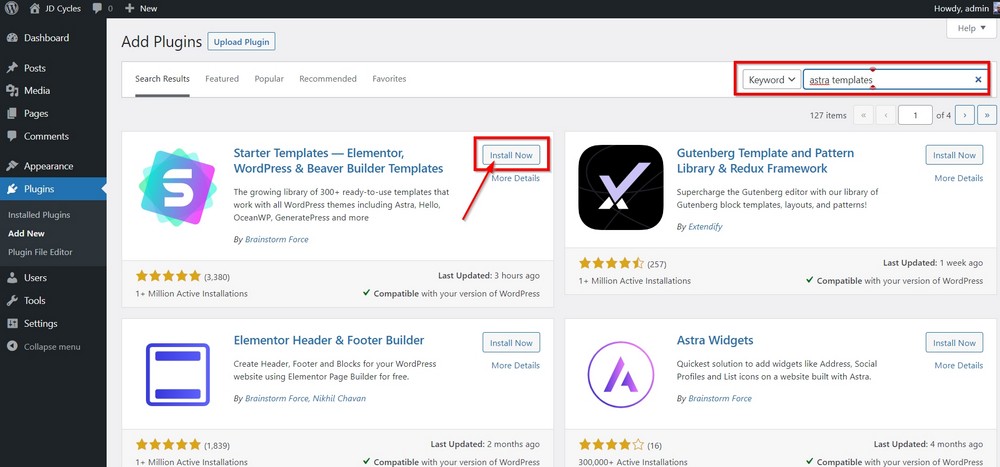
Go to Plugins > Add New and type ‘Astra Templates’ in the search box to locate the plugin.
Press the Install button and then Activate the plugin.
B: Choose a template
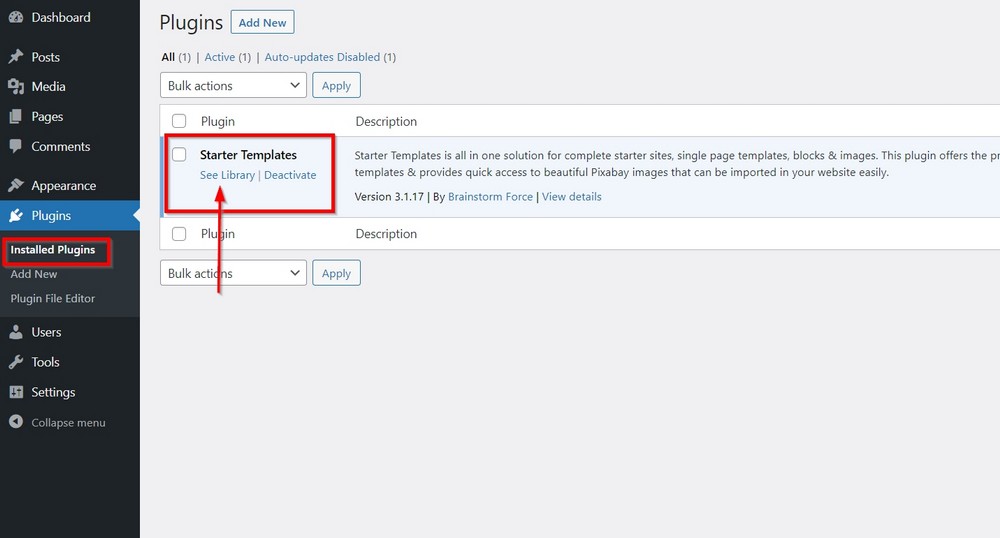
Go to Plugins > Installed Plugins to find Starter Templates.
Click on See Library. The next page should display an introductory video.
Click on the blue button underneath that says Build Your Website Now.
On the next screen, choose the page builder of your choice. For this tutorial, we will select Block Editor (Gutenberg).
The next screen will show the predesigned templates you can choose for your website. Search for something relevant to your business.
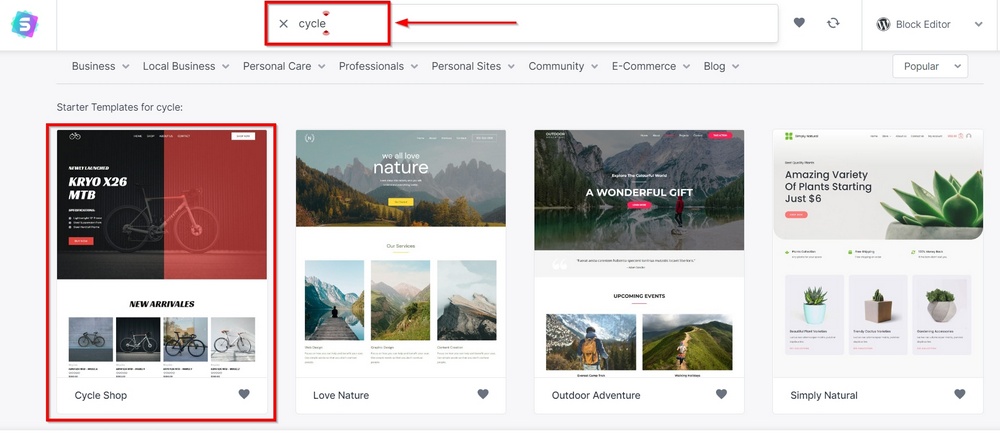
For our example, we’ll type ‘cycle’ in the search box and select the Cycle Shop template. It matches what we want to do on our website.
The process will be exactly the same whichever template and whichever page builder you choose.
On the following screens, the template import wizard will walk you through a couple of essential steps:
- Upload logo
- Change fonts and colors
- Import sample content along with the template
We suggest importing the sample content to help you see how your site will look after the import process.
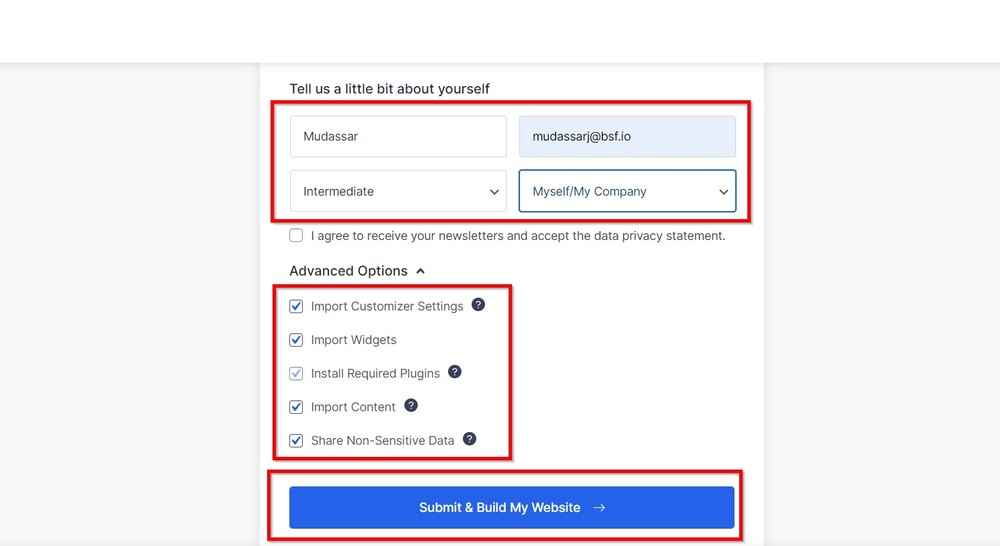
Press the blue Submit & Build My Website button on the last screen.
The process should complete in just over a minute.
You will notice that Astra has installed a few relevant plugins.
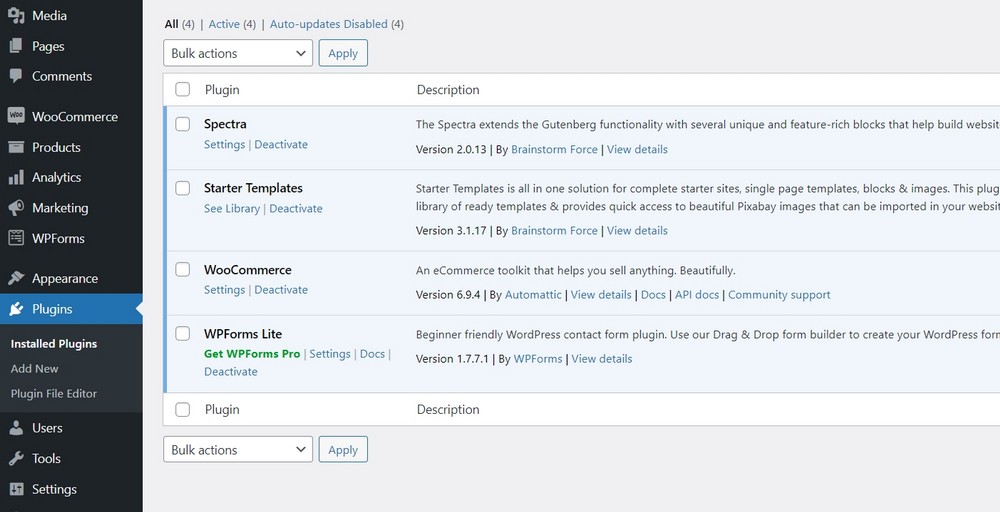
Go to Plugins > Installed Plugins to find Spectra, WooCommerce and WPForms Lite in the list.
Spectra is developed by us at Brainstorm Force to extend Gutenberg functionality.
If you select an Elementor theme, Astra will install the free version of the Elementor page builder instead of Spectra.
WooCommerce is the best plugin for eCommerce, and WPForms Lite can create different forms and help connect with your audience.
Similarly, the new template has added all essential pages to your site for eCommerce and connecting with your audience.
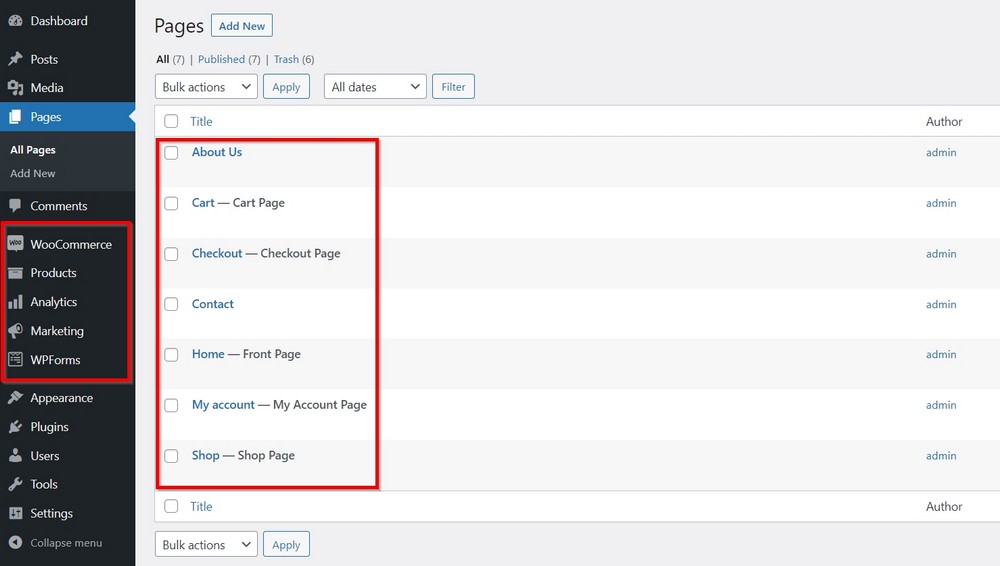
You can use the existing design as it is or customize it as you see fit.
Let’s walk you through a little customization.
C: Customize parts of your new template
It’s easy to customize an Astra template without touching a line of code.
Let’s change things our way from the following segments:
- To customize the header, go to Appearance > Customization > Header Builder. You can repeat the same process for Footer Builder
- If you want to change how a single page and archive pages should look, go to Appearance > Customization > Blog
- Whether you want to go with a sidebar on your site or not, you can change the layout from Appearance > Customization > Page
We recommend spending a little time familiarizing yourself with how everything works. It’s easy to learn and provides limitless customization options.
11. Create or edit categories
Categories are essential for keeping things organized if you plan to run a blog on your site.
Before creating categories, we advise you to research which terms and keywords are most relevant to your business.
If you sell bicycles on your site, do you plan to guide people about the technology cycle manufacturers use or how to keep bicycles rust free?
Or maybe you would like people to know how to distinguish between different types of bicycles.
Stuff like that.
So, to create a category called How To, go to Posts > Categories and enter the category name in the name field.
Write the same in small in the Slug with a hyphen between words and briefly describe the category in the Description field.
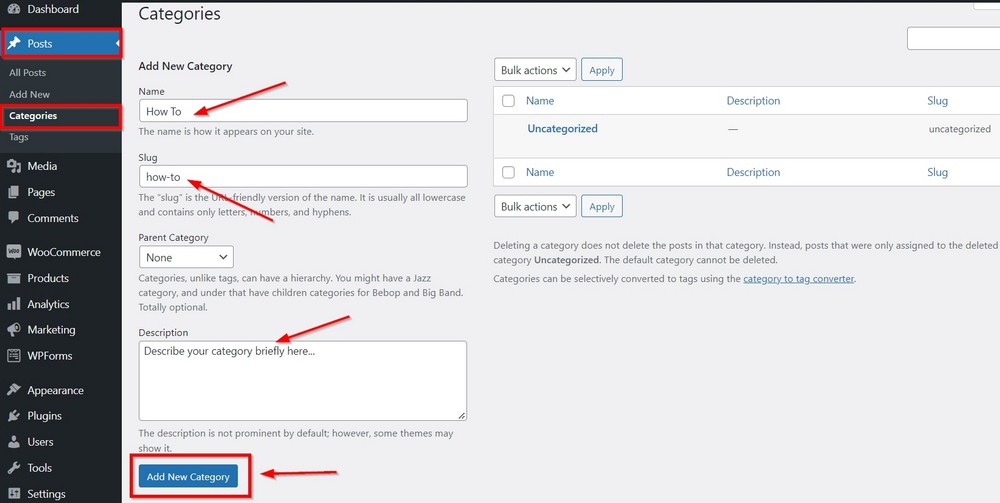
Press the button Add New Category when you are done. It will add the new category to the list.
Note:
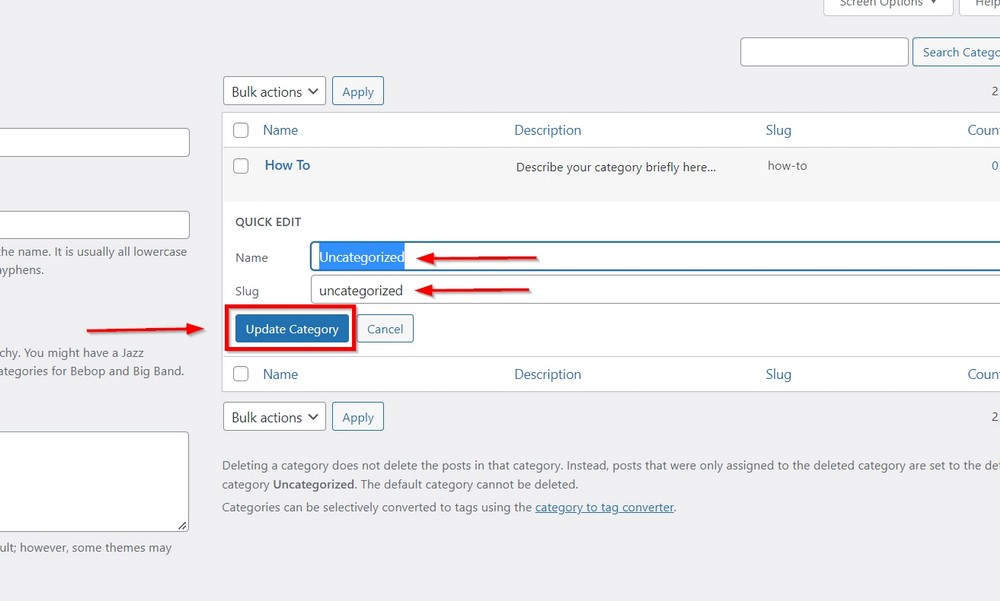
Alternatively, you can create your first category by renaming the default category Uncategorized.
Click on the Edit or Quick Edit menu under the category name and change the name and slug field the way you want.
12. Create menus
Menus are essential to help people navigate your website and are a vital element of creating a great user experience.
You can go one step further by activating mega menus to accommodate huge content and giving your menus a visual appeal. You can give them different shapes and colors effortlessly with Astra.
You can access menus in multiple ways.
One is to reach through Appearance > Customize > Menus. We chose this method because you can see changes happening in real time.

You can see how the Astra template has created and arranged menus on your site.
Out of the five menus we can see in the left sidebar, we aim to add our menu item in the Primary Menu linked to the header area.
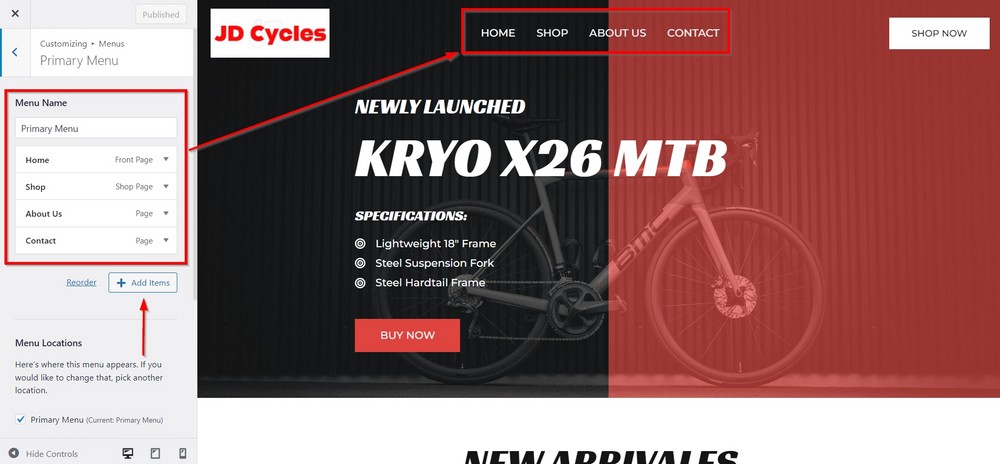
Click the menu to reveal menu items inside.
Press the Add Items button that will slide out a pan with all the items you currently have on your site.
Select the ones you want to show in the primary menu bar. We will click on Categories and choose the desired menu item.
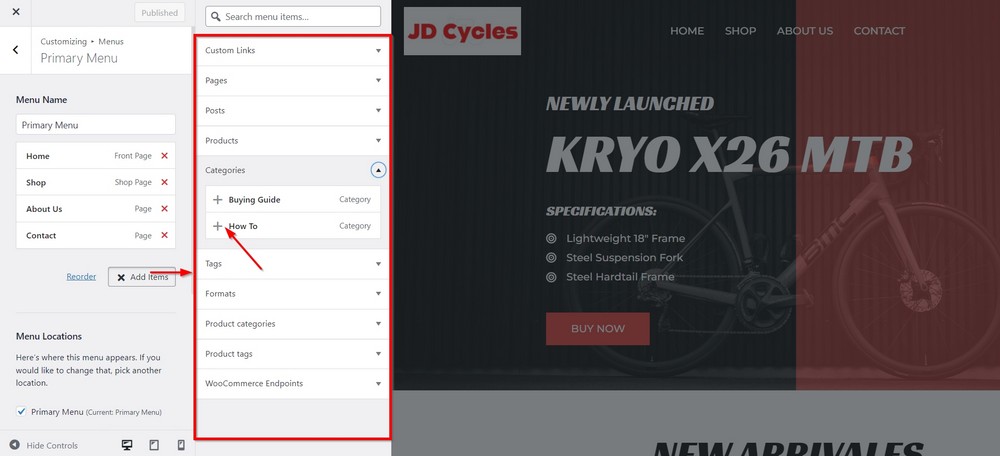
You can see how easily we added a new menu item in the header area that is also visible in the sidebar.
Press the Publish button in the top left corner for the changes to take effect. Press the x icon to come back to the WP admin area.
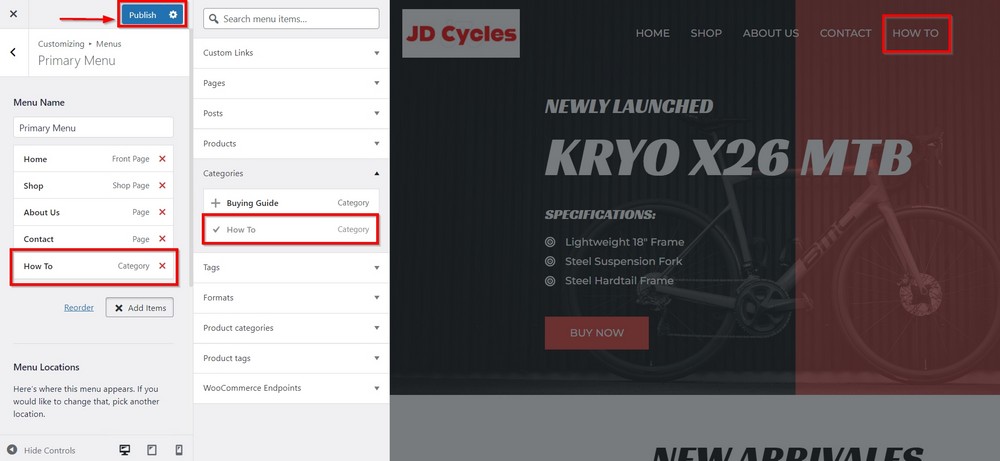
Similarly, you can add or remove menu items in all the menu positions your theme has created.
This is not the only way to edit your navigation.
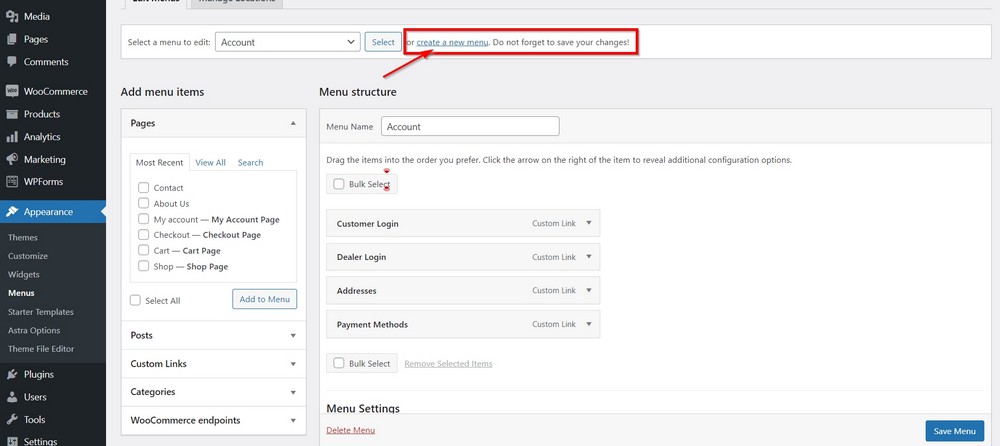
You can also create a custom menu and link a different set of items to it.
To do this, go to Appearance > Menus, click on create new menu and name it accordingly.
Choose any number of display positions from Menu Settings.
Press the Create Menu button visible at the bottom right corner. You can add different menu items later as required.
13. SEO optimization
One of the best things you can do at the beginning of your journey is to optimize your site for search engines.
This will create more possibilities for you to get a better search engine ranking and bring more traffic to your site.
We suggest installing the Yoast SEO and Schema Pro plugins. They are the top performers in the WordPress community and a great combo to improve your website’s SEO health.
Maybe you plan to cover a variety of topics on your website, such as reviews, articles, food recipes, or anything your reader would love to read.
Schema Pro defines the content correctly, making it easier for search engines to understand and rank it accordingly.
For your reference, here’s a complete tutorial on Schema Pro:
With Yoast, you can get all essential features for free. You can install it by clicking on Add New under the Plugins menu.
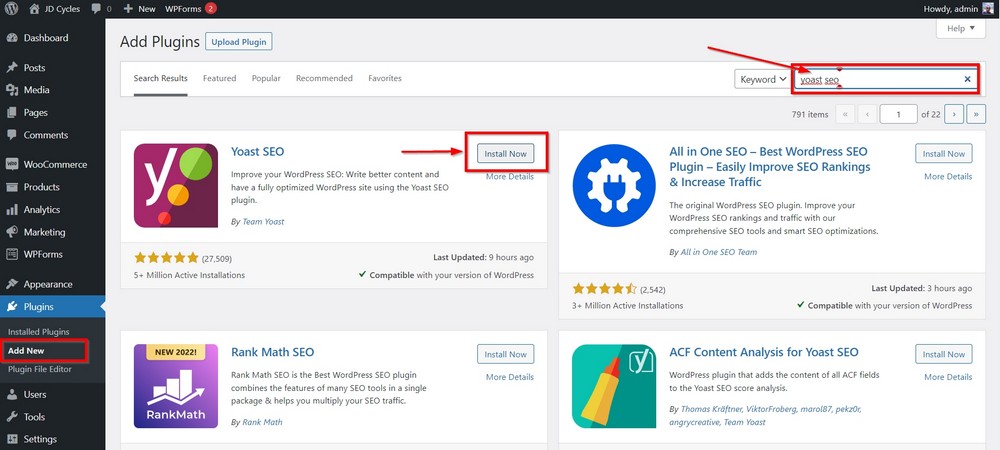
Type ‘Yoast SEO’ in the search bar to locate the plugin.
Press the Install Now button and then Activate when the option appears.
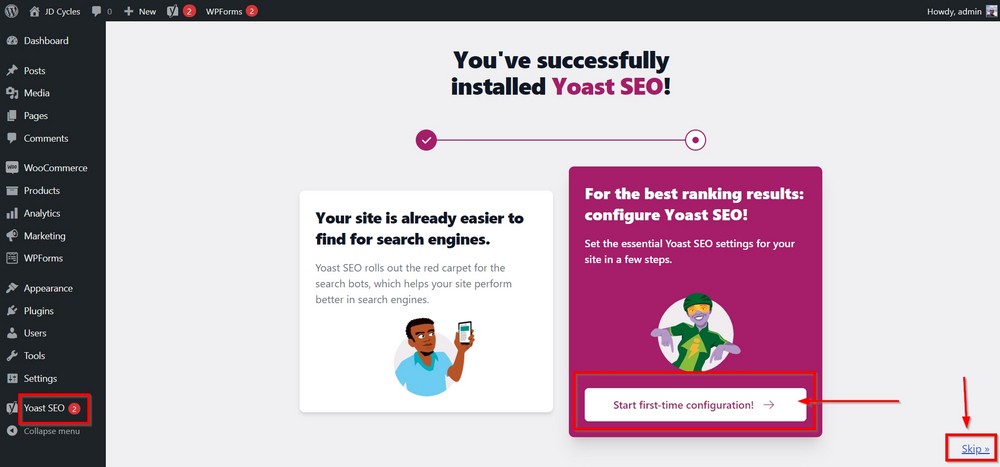
You will notice Yoast adds its own menu in the left sidebar. Its installation wizard is beginner friendly that walks you through every essential step to configure it easily.
You can also press the Skip link to leave the wizard and configure the plugin manually if you prefer.
We suggest using the wizard for ease and recommended settings.
If you press the Skip button mistakenly, worry not, you can always restart the wizard by clicking on Yoast SEO First-time configuration from the Yoast notification banner on top of the page.
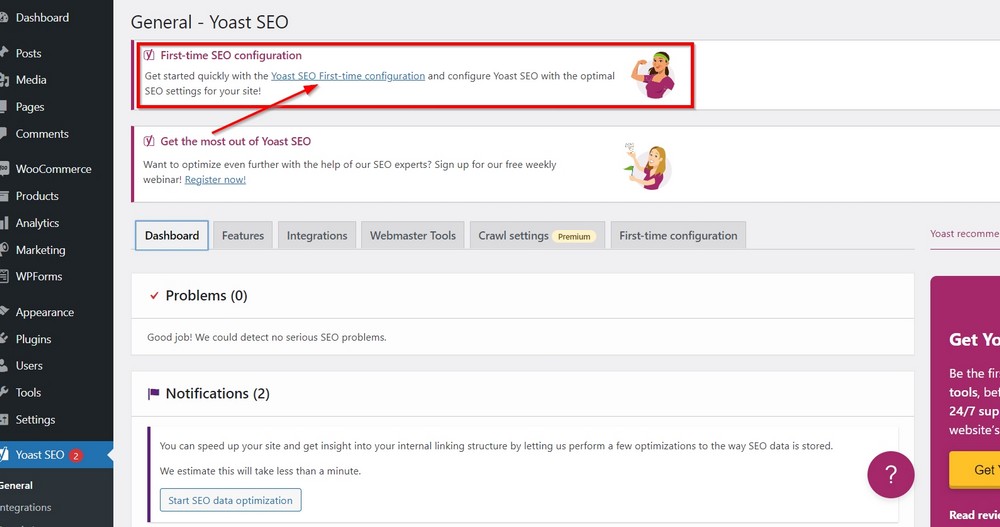
14. Set up Google console
Google is the largest search engine in the world with around 83% market share. That means Google can bring you lots of organic traffic.
Google will only index your site when you ask it to do so. The best way is to set up the Google console.
This step should be among your top things to do after installing WordPress.
You can do it with or without Yoast’s help. Since we have already installed Yoast, it’s much better to use its feature to connect our sample site with Google.
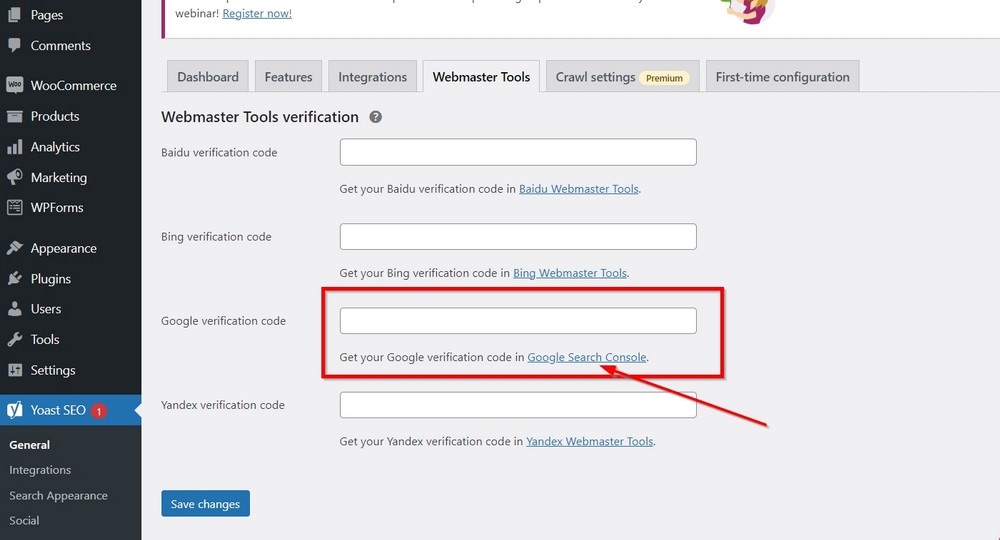
To do it, go to Yoast SEO > General > Webmaster Tool to locate the Google verification code.
Click on the Google Search Console link to access Google Webmaster Central.
Google would like to verify you as the legit owner/representative of the website. It does this through one of the four methods it lists on its verification page.
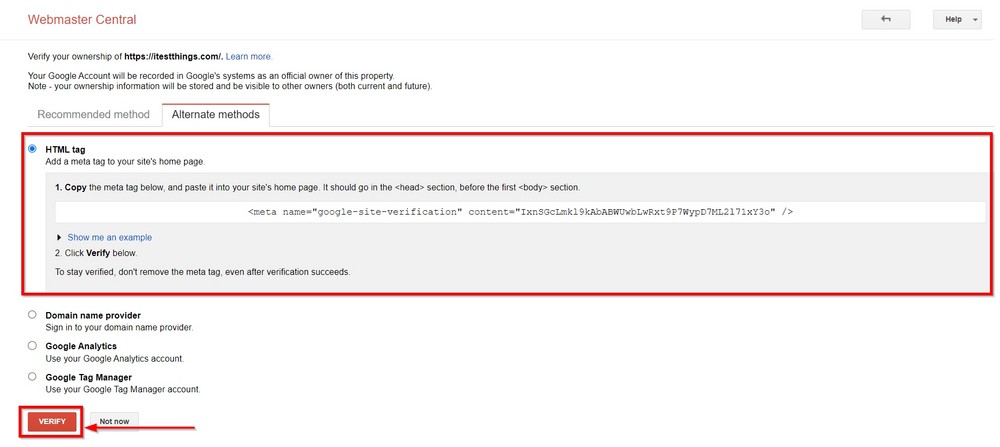
We will use the HTML tag method. This asks to copy the meta tag into your site’s homepage.
A shortcut is to copy the tag and paste it into Yoast’s Google verification code field.
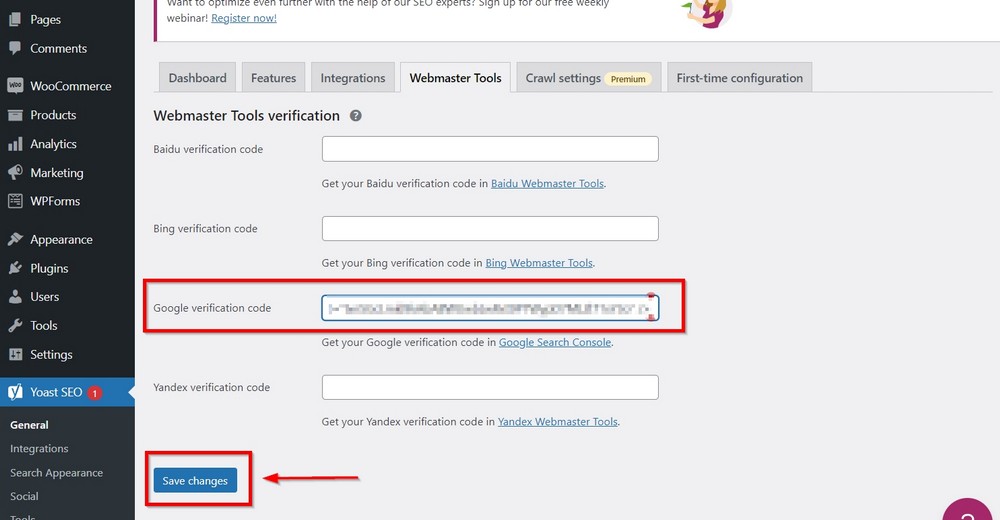
Press the Save changes button.
Next, press the red Verify button after successfully entering the meta tag inside Yoast’s field.
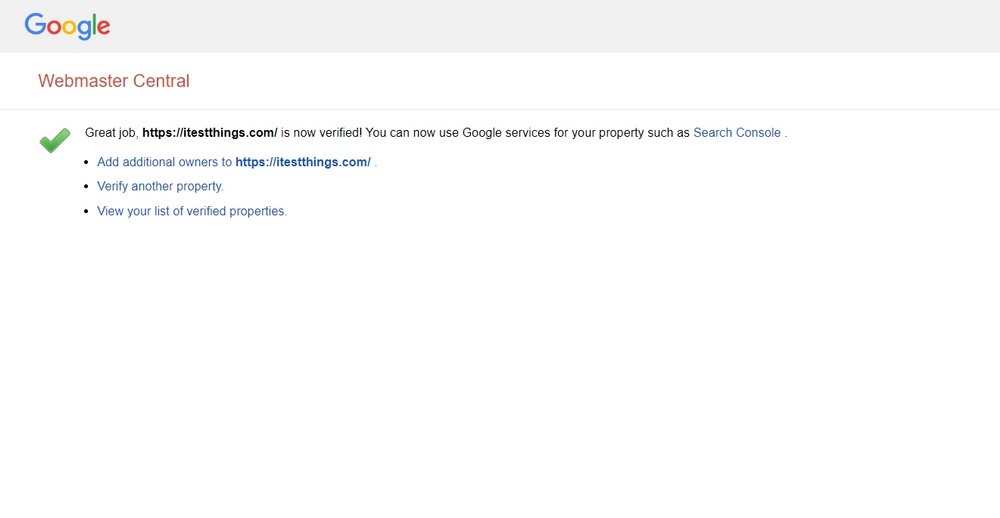
You should see a success page similar to the following image.
Sometimes, Google may add an additional verification step. It may ask you to put a code in your registrar’s DNS entry field.
If these words scare you, don’t worry, you can always ask your domain registrar’s support to do it for you.
15. Submit a sitemap
One of the good things about Yoast is that it creates an XML sitemap for your site. You should submit one to search engines to help them navigate and index your site once it’s complete.
With Yoast on your website, you can find your sitemap on the following link.
https://yoursitename.com/index.php/sitemap_index.xmlSubmit the link in the Google console sitemap area, as shown in the following screenshot.
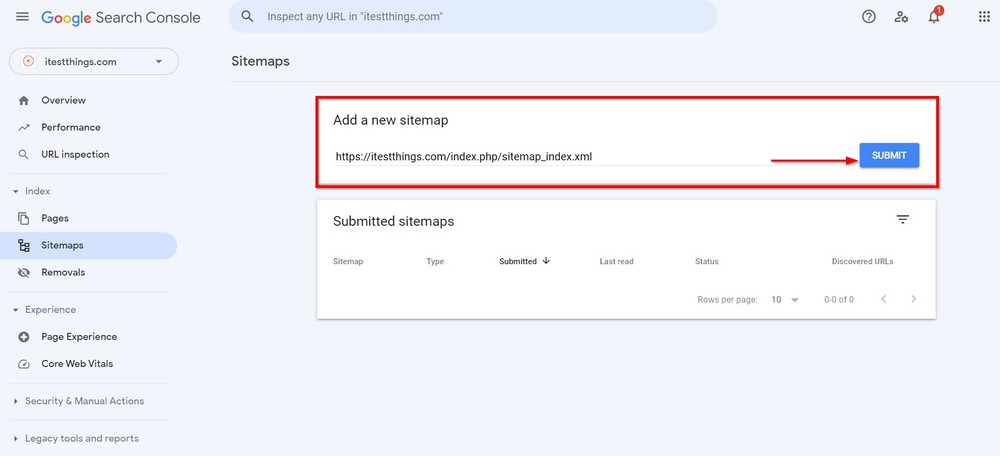
16. Robots.txt file
A robots.txt file tells search engines what they need to index on your website and what not to.
For example, if you want them not to index /thank-you/ page, you need to disallow it in the robots.txt file.
It’s a powerful tool that can make or break your website.
As a beginner, you don’t need to create a robots.txt file. WordPress creates a virtual file with every install that carries a standard crawling rule.
As we have Yoast installed on our site, it has automatically edited the virtual robots.txt file for us with its recommended rules.
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://www.yoursitename.com/sitemap_index.xmlYou can find your virtual robots.txt file on this URL https://www.yoursitename.com/robots.txt
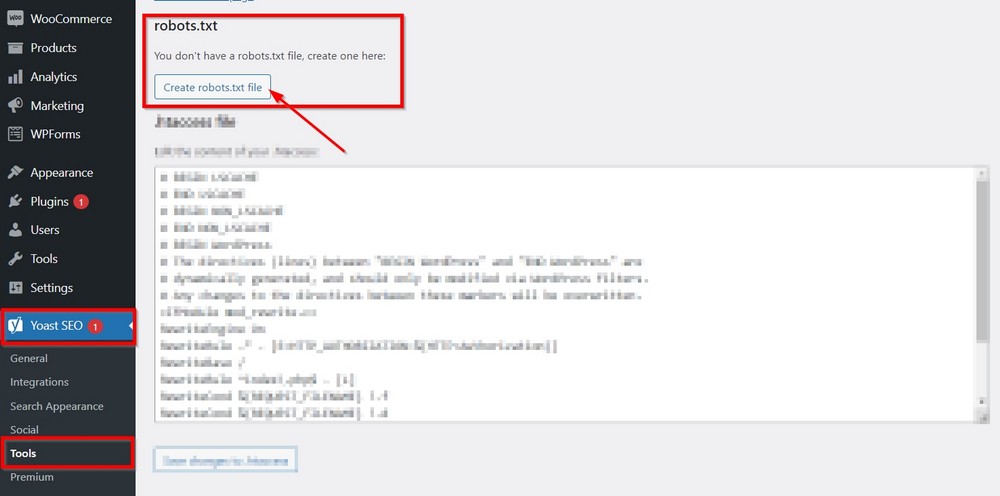
Creating a physical robots.txt file is more straightforward with Yoast.
Go to Yoast SEO > Tools > File Editor and press the Create robots.txt file button. That’s it.
You can edit the file from here and add/remove anything you want for your site.
17. Google Analytics
Without an analytics tool, it’s impossible to properly track the progress of your website. These tools are usually premium, but fortunately, Google Analytics (GA) is free.
It keeps track of your website and gives you lots of valuable information in a user friendly way.
GA informs you about your customer behavior, user interaction, content performance, traffic sources, user location, and so on.
With these reports, you can create the best development strategy for your site.
To integrate Google Analytics with your site, you must first sign up. The process is really simple if you already have a Google account.
Type https://analytics.google.com in your browser and complete the process through a wizard.
You can use these detailed guides on adding Google Analytics to your site without a plugin, with a plugin and for WooCommerce sites.
18. Website security
Whether you run an eCommerce site, blog, or portfolio website, security is paramount. You need to take it seriously from day one.
WordPress is relatively secure, but as so many websites use it, it’s a target. The more layers of protection you have, the more secure your website will be.
Here are some useful plugins to make your site a hard nut to crack.
To install these plugins, you need to go to Plugins > Add New and type the name in the search box.
You will see the desired plugin on top of others. Press Install Now and Activate after that.
A: Wordfence
The Wordfence plugin has been downloaded over 4 million times and offers excellent security features in its free version.
Tools include malware scanning, website firewall and live traffic monitoring.
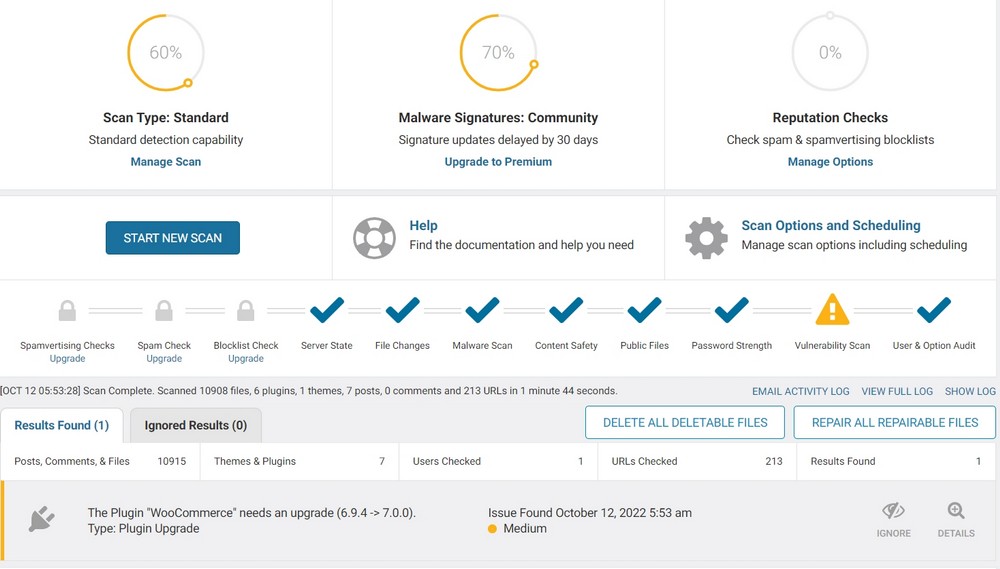
You can also enable two factor authentication for a few or all user roles.
B: Akismet
Akismet is the most widely used plugin to fight spam comments. It’s a must-have security tool for sites looking forward to engaging with their users but don’t want to get stuck dealing with spam comments.
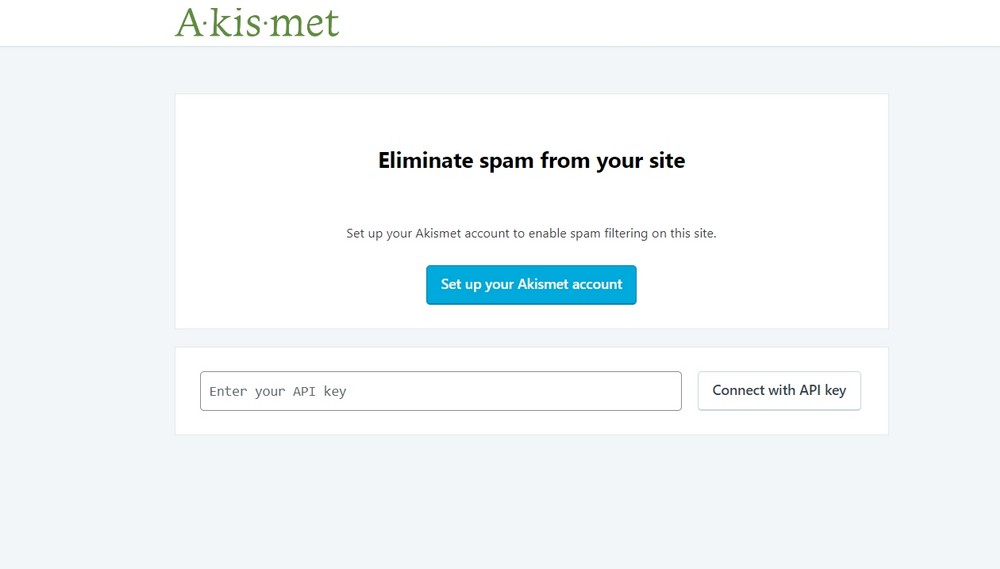
Akismet works perfectly with the settings we did earlier in the Discussion segment.
Its simple interface requires only the API Key and that’s it. You can choose between marking suspicious comments as spam or moving them to trash.
With Akismet installed, you can automatically reduce spam comments on your site by over 90%.
C: UpdraftPlus
You spend extensive time and energy to prime your site for success. What if it gets hacked or wiped for reasons out of your control?
It’s imperative to create a backup plan.
This is one of the most crucial things to do after installing WordPress.
With over 6,000 five star reviews and more than 3 million downloads, UpdraftPlus is one of the top backup solutions for your WordPress website.
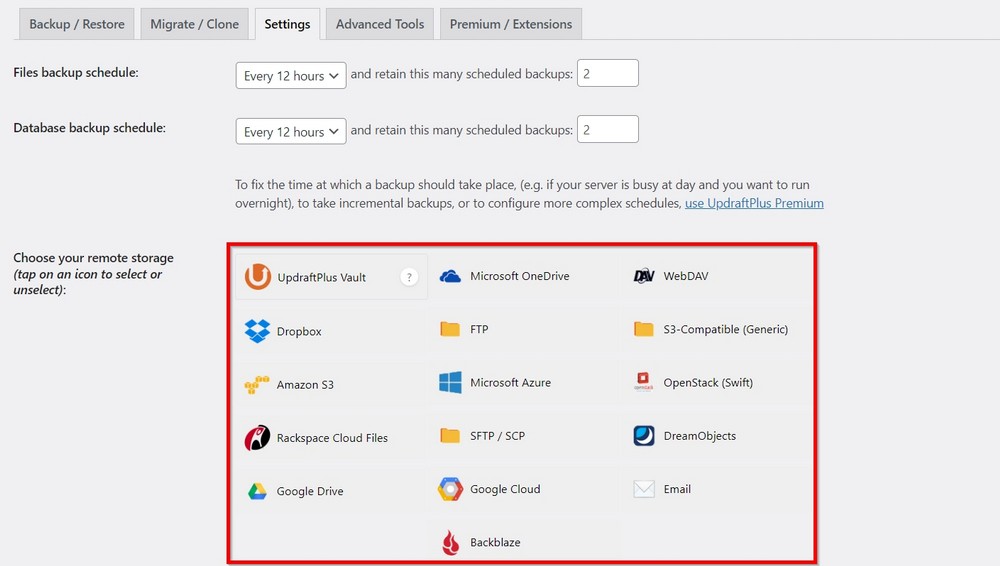
With the free version, you can schedule your backups and store them directly in Dropbox, Google Drive, Amazon S3, Rackspace Cloud, FTP, OpenStack Swift and more.
19. W3 Total Cache for website performance
Caching speeds up the performance of your website without making any actual changes.
You will find many cache plugins on the WordPress repository, but W3 Total Cache is a leading contender to boost your site’s performance.
Your website speed and core vitals are essential for the user experience and SEO activity. The faster it is, the more popular your site will become for users and for search engines.
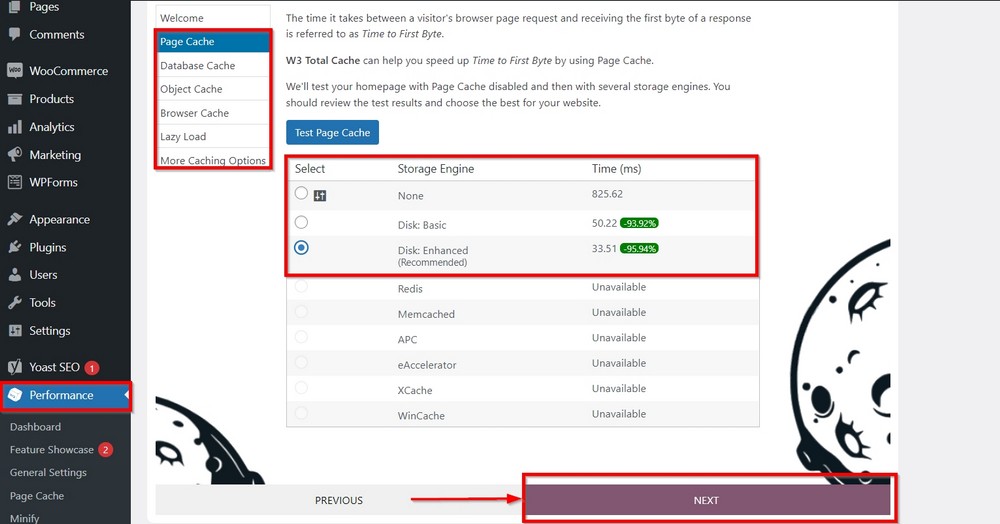
If you are a beginner, the plugin’s starting wizard walks you through all segments and helps you easily configure the most essential settings.
20. Optimize for conversion
Conversions are essential, whether it’s a call to action banner for subscribing to a newsletter or buying a product.
It’s a reward you get at the end of a campaign.
Whether you want to communicate with users before conversion or after they make a purchase, you will need some plugins to communicate.
A: FluentSMTP plugin
This free plugin works perfectly with email service providers to ensure your email reaches subscribers.
If you plan to use email to reach out and build a following, this plugin makes everything easier.
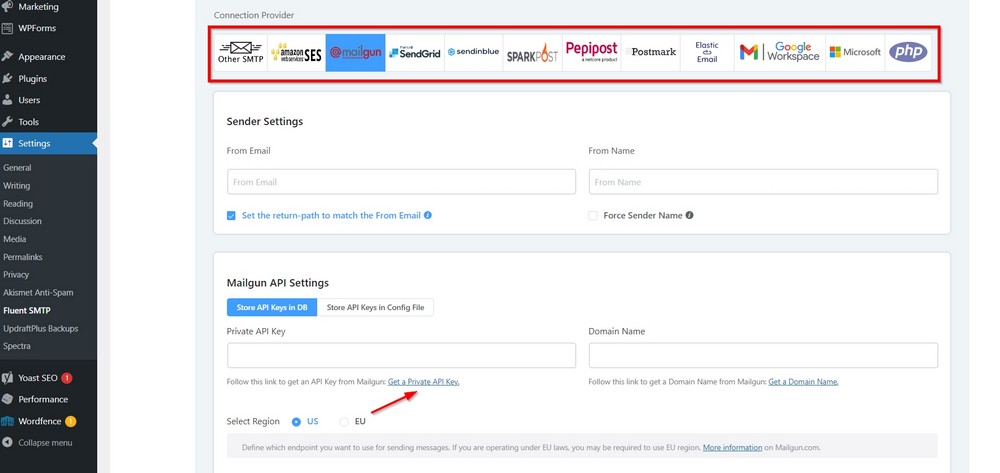
After installing the plugin, go to Settings > Fluent SMTP and open its settings page.
Select the connection provider from the list and enter the relevant information in the fields.
B: Set up a contact form
One of the benefits of installing Astra is that it adds prebuilt contact pages with integrated contact forms using WPForms Lite.
If you want to add additional forms for other pages, you can go to WPForms > All Forms/Add New and create a form as required.
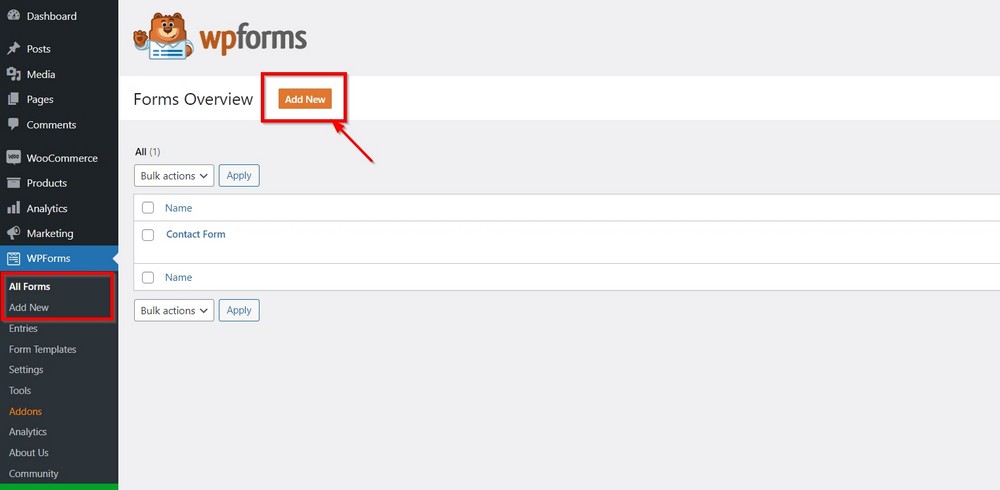
Let’s create an opt-in form so you can see the process in action.
Hover the mouse over the form and press the Use Template button.
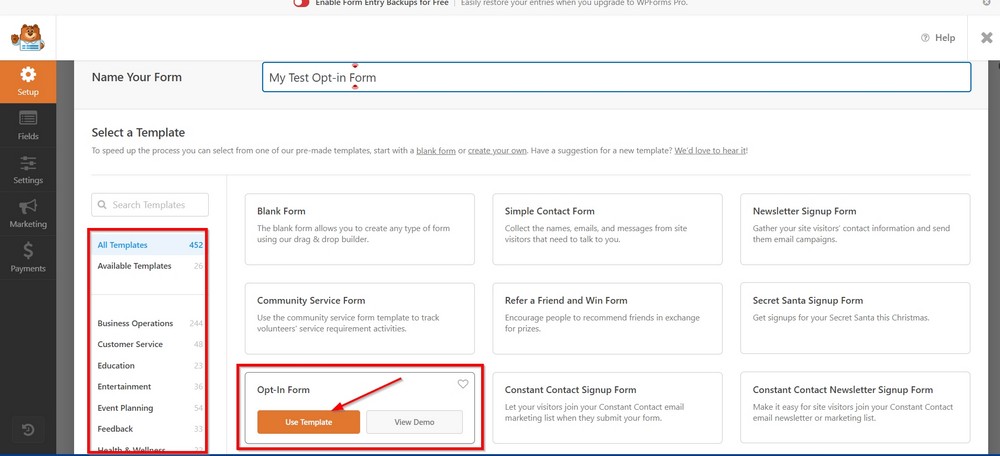
On the next screen, you can customize the form as you need.
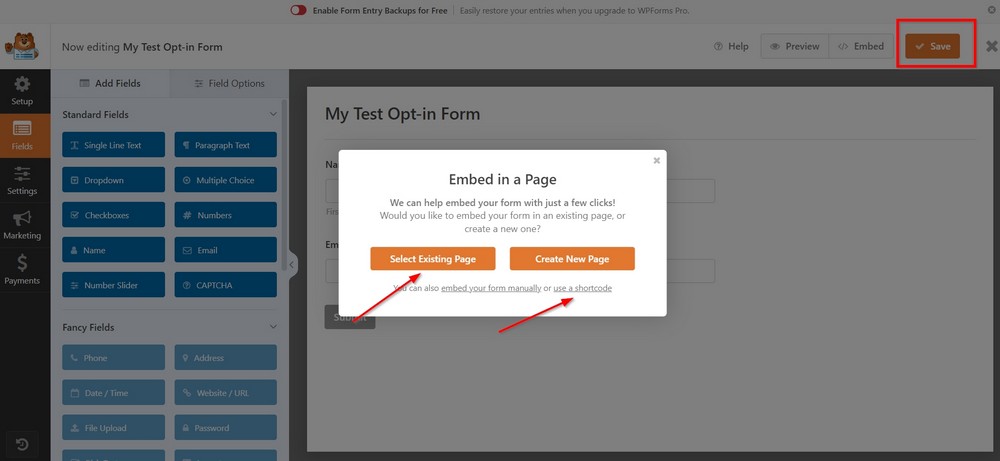
Once done, save the changes.
You can place the form on an existing or new page or use the shortcode to place it anywhere you want on your site.
21. Privacy policy
When you run a website, you interact with users and collect information. It could be your contact or subscription form, analytics monitoring, shop page, or anything your user interacts with.
You should ideally disclose how you collect the user’s data and what you do with it. You should also mention your compliance with relevant national and international privacy laws.
You can create privacy policy documents in several ways, including:
- Use the default privacy policy page WordPress adds at the time of installation
- Get services online from professionals
- Install plugins like WP AutoTerms and Complianz
22. Create users
For a larger website with more contributors, you may need to create multiple users and assign them different roles depending on their responsibilities.
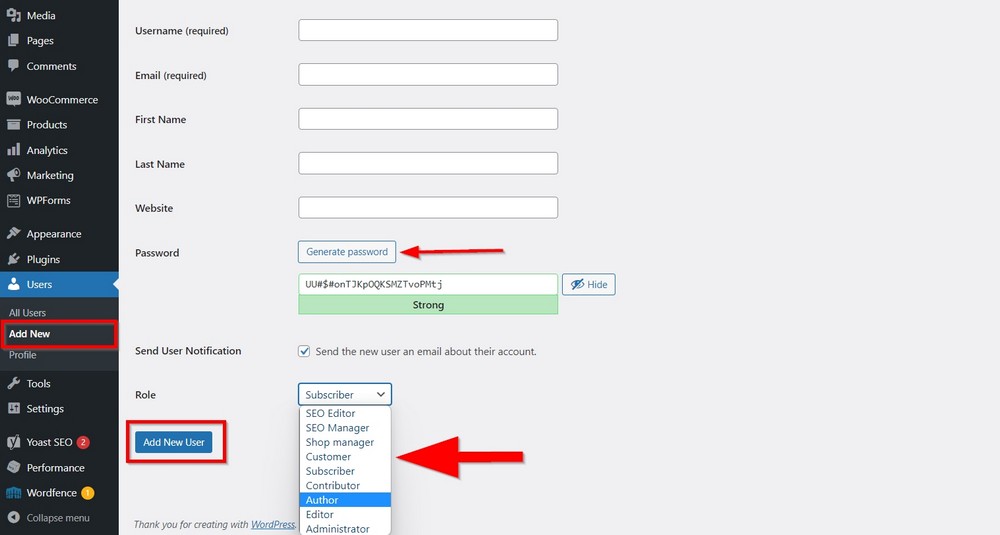
To add a user, go to Users > Add New to open a form for creating a new user.
Assign a unique user name and role from the drop down list.
Use Generate Password to create a secure password that is hard to guess by others.
Once done, press the Add New User button.
Note:
You can always come back to the user list from Users > All Users and edit the details. In the edit mode, the user page will show you a large number of options for adding more information to their profile.
23. Publish a post
We love WordPress for making it super easy to publish posts and pages.
Let’s add a new post.
Go to Posts > Add New, or you can access the page from the top toolbar.
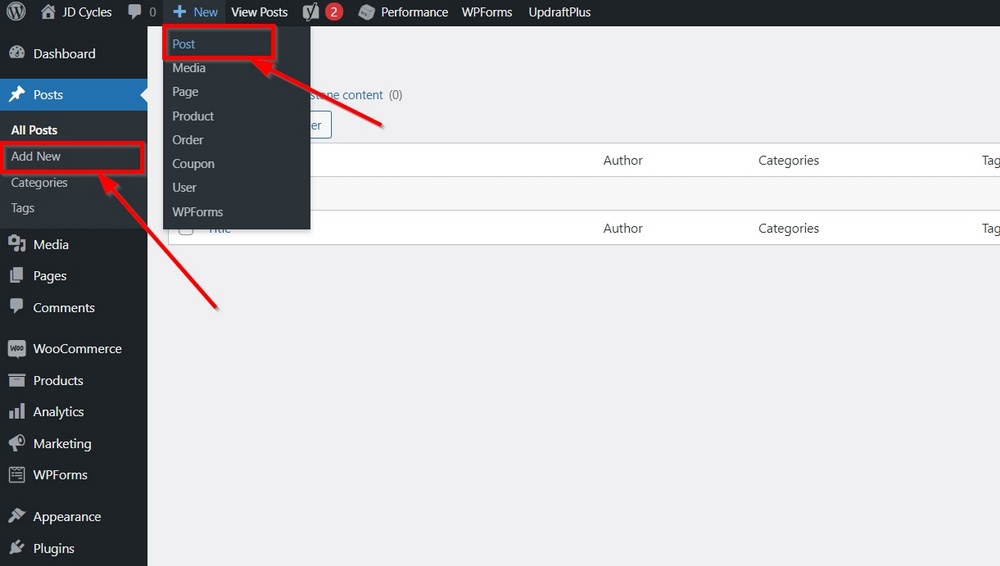
It will open the WordPress post editor (Gutenberg) on your screen.
It may look a little overwhelming at first, but trust us, it’s where you will spend most of your time creating, editing, or formatting your posts.
Learning how to create and format posts is one of the most interesting things to do after installing WordPress.
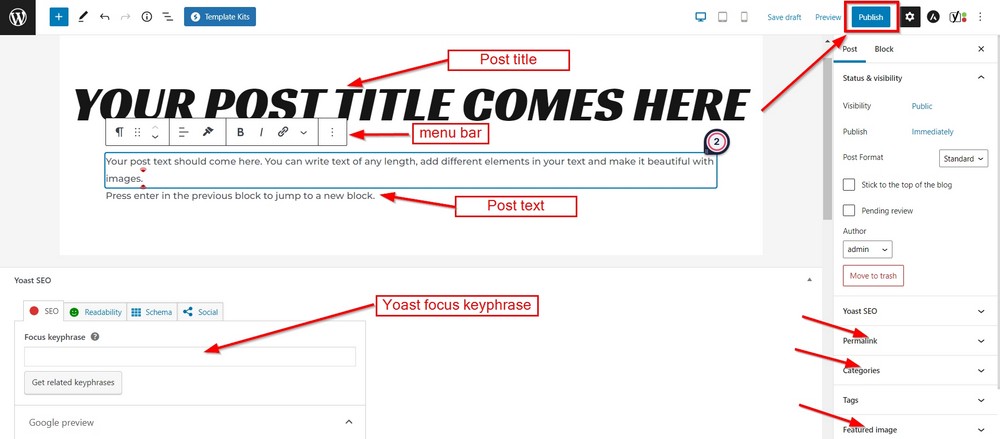
You will notice that the editor screen is divided into two main sections.
The left is the content area where you add the content, and the right sidebar holds the post/page and block settings.
Every selected block in the content area gives you access to a small toolbar on top of it. The sidebar also opens related settings for the block.
Now add some content, including title, text, and feature image.
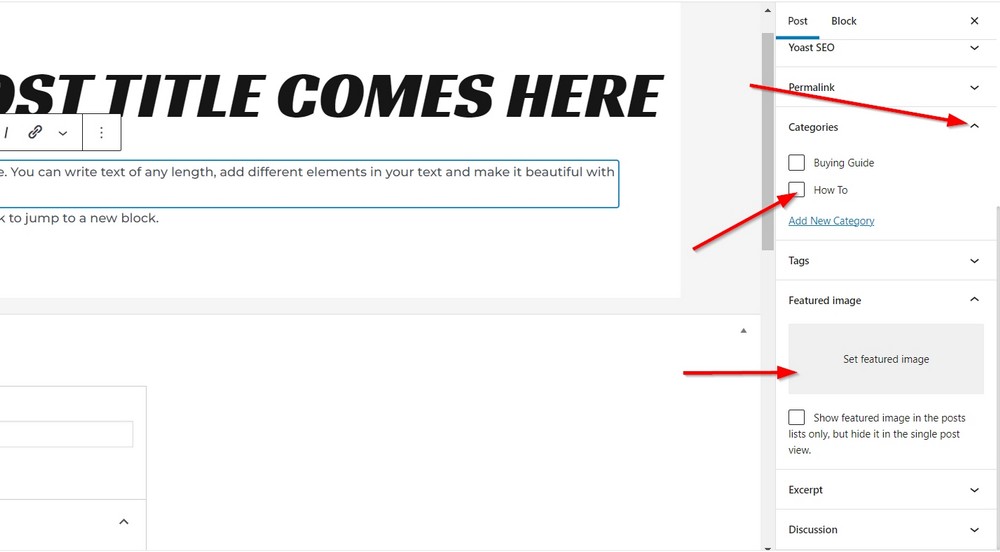
Select a relevant category and press the publish button to make your post live.
Here are a few things you should check before hitting the publish button:
- Title of the post
- Featured image
- Edit permalink (if you want to make it short and SEO friendly)
- Category
- Excerpt
- If you are using Yoast, don’t forget to add focus keyphrase, slug and meta description
24. Limit post revisions
While you edit the post, the autosave feature of WordPress keeps creating different copies of it. They are called revisions.
It’s a helpful feature to undo changes we don’t want and allow us to choose an earlier saved draft.
WordPress autosaves a new draft every 60 seconds for each post which can pile up and swell your database over time.
Fortunately, we have solutions to deal with it and limit the number of revisions.
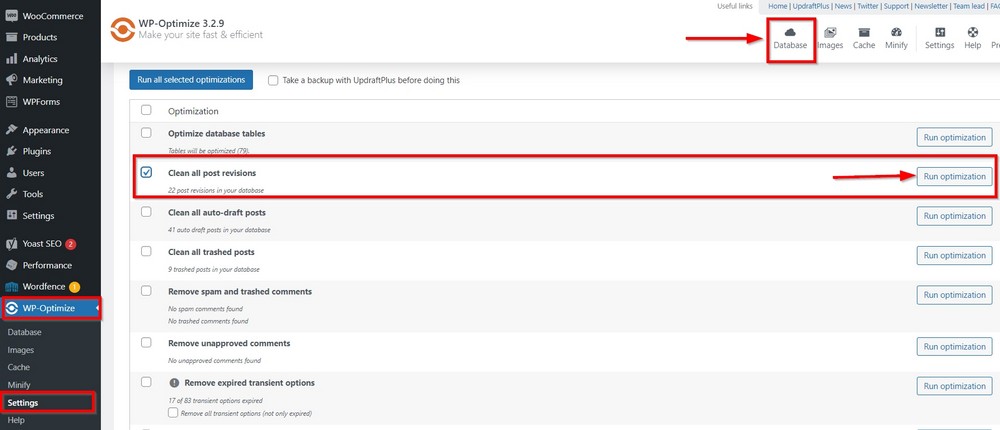
A: WP-Optimize plugin
Plugins like WP-Optimize provide an easy way to delete the revisions.
Install the plugin and click on the Database module from the Settings area.
Check the box next to Clean all post revisions and press the Run optimization button to remove all the revisions.
B: Stop post revisions by adding a rule
If you don’t want to use a plugin, add the following rule in your wp-config.php file to stop WordPress from creating revisions.
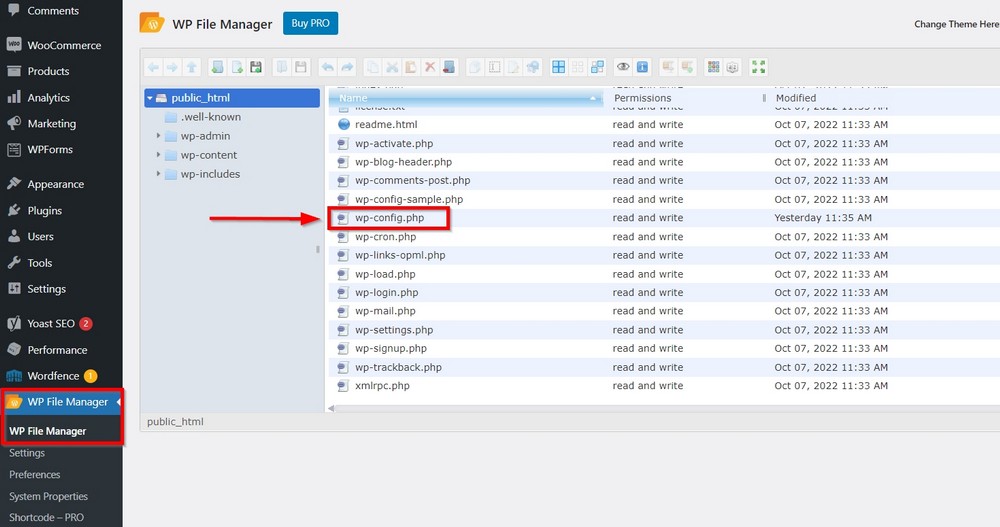
define (‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’, false );You can access the wp-config.php file in your WordPress root directory either through a plugin such as File Manager or accessing it through your web host.
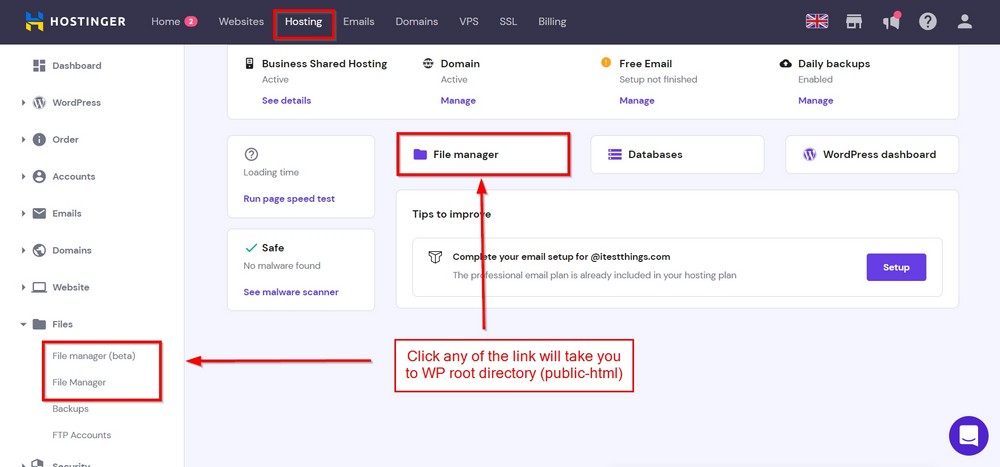
If you are on Hostinger like us, you can find File Manager on the Hosting page.
You may see the public_html folder on the next screen. Open it and locate wp-config.php to add the above rule.
You can choose to add it just before the following comment /** Absolute path to the WordPress directory. */.
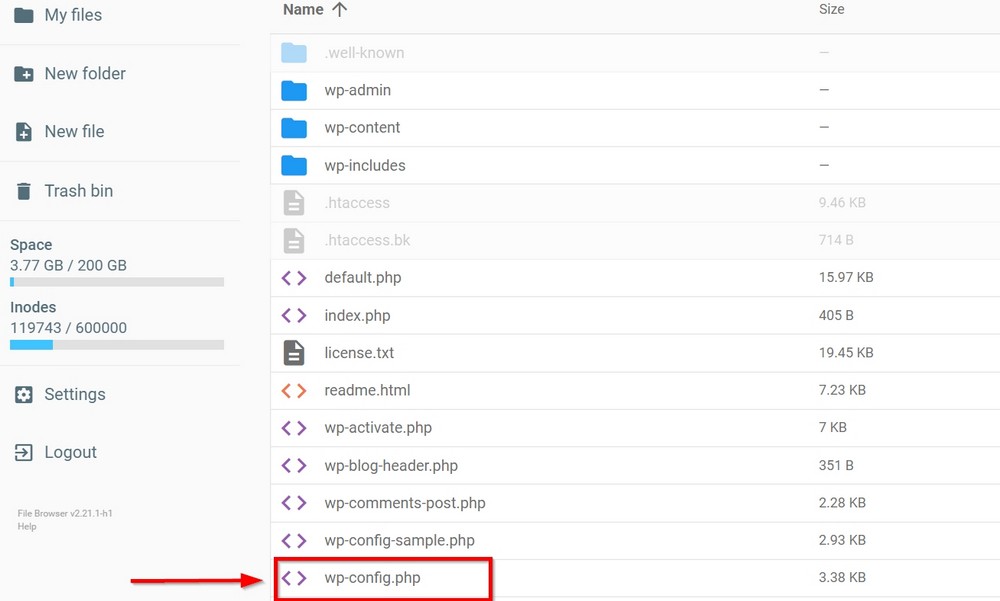
Add the rule and save the file.
With the File Manager plugin, you can access the wp-config.php file by clicking on WP File Manager.
25. Set up ping services
Ping is the tool that WordPress uses to tell search engines that the site has updated content. It actually invites search engines to crawl.
And as WordPress recommends, you can add certain services in the Update Services field that you can locate inside Settings > Writing.
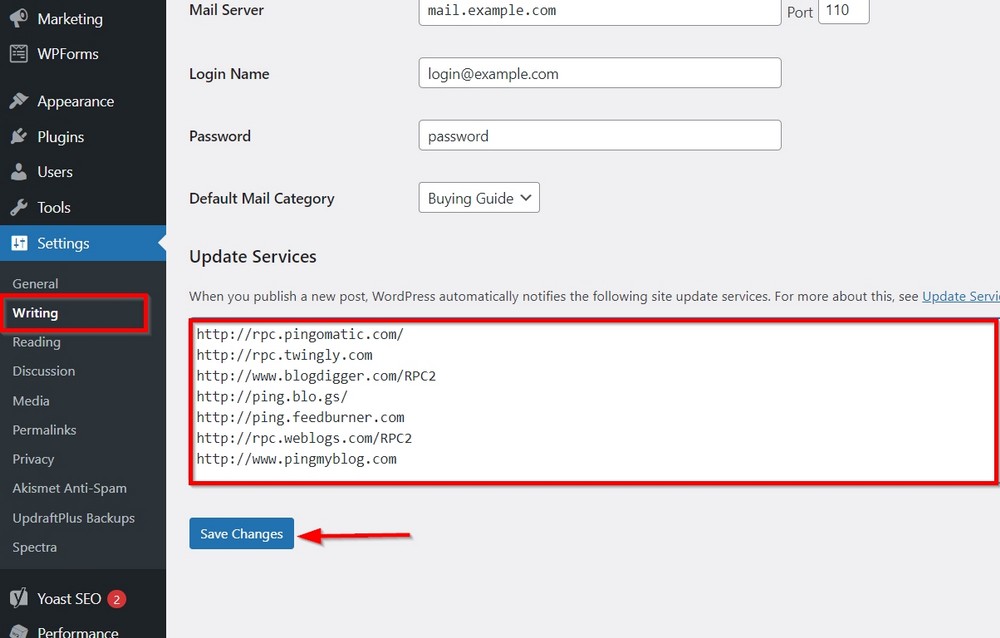
Here is the list of services to add after installing WordPress. Once done, don’t forget to press the Save Changes button.
- http://rpc.pingomatic.com/
- http://rpc.twingly.com
- http://www.blogdigger.com/RPC2
- http://ping.blo.gs/
- http://ping.feedburner.com
- http://rpc.weblogs.com/RPC2
- http://www.pingmyblog.com
Note:
Certain web hosts don’t allow you to use the ping service. If your host limits you from using the service, you can use Feed Shark, a free tool that pings over 60 services.
26. Brand your login page
If you are an agency or a developer, you would likely wish to customize the branding before handing over the website to your client.
You can do it manually with your coding skills, but an easier way is to install a free plugin.
Here are some best choices for you to brand the login page:
This is purely optional but can be a nice finishing touch to a project that sets you apart from the competition.
Final Thoughts
Your website should load fast, be feature rich, hard to hack and be easy to interact with. These are the building blocks of a successful website.
An easy way is to follow the steps in this guide immediately after installing WordPress.
That way, you have the basics fully covered and your website will be ready to amaze, entertain or make you some money from the outset.
What do you think of these tips? Did we cover everything? Have any other tips you think we should include? Share your experience with us in the comments.